Introduction
The project management triangle, also known as the triple constraint model, is a fundamental concept in project management. It represents the delicate balance between scope, time, and cost in delivering a high-quality project.
This model is crucial for project managers to navigate complex projects successfully. By understanding and managing these three interconnected constraints, project leaders can make informed decisions and adapt to challenges effectively.
These constraints are interdependent; altering one inevitably affects the others. Effectively managing the project management triangle enables teams to optimise resource allocation, manage stakeholder expectations and deliver successful outcomes.
By grasping this concept, project managers can steer their initiatives towards success, even in the face of unforeseen obstacles.
Understanding the project management triangle
The three constraints explained
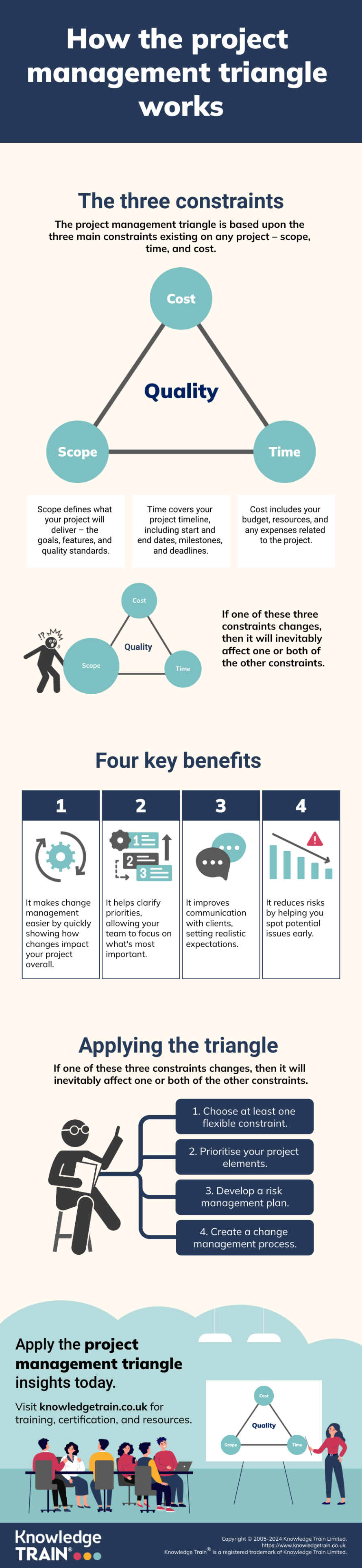
The project management triangle comprises three essential constraints: scope, time, and cost. Each plays a crucial role in shaping project outcomes.
- Scope: This constraint defines the project’s boundaries, objectives, and deliverables. It encompasses project goals and requirements, specific features and functionalities and quality standards and expectations.
- Time: The time constraint relates to the project’s duration and schedule. It includes project start and end dates, milestones and deadlines and also task sequencing and dependencies.
- Cost: This constraint involves the financial and resource aspects of the project. It covers budget allocation, human resources and labour costs and equipment and material expenses.
Relationship between constraints
The three constraints are interconnected and mutually influential. Altering one constraint invariably affects the others. For instance, expanding scope often requires more time or resources, reducing time may necessitate increased costs or reduced scope and limiting costs might impact the project’s scope or timeline.
Project managers must continually balance these constraints to maintain project integrity.
Impact on project quality
The equilibrium of scope, time, and cost directly influences the project’s quality. Optimal balance leads to high-quality outcomes, while imbalance can compromise results. Consider the following scenarios:
- Rushed timelines may lead to subpar deliverables
- Limited budgets might force cuts in essential features
- Overambitious scope can strain resources and timelines.
Successful project management involves strategic trade-offs among constraints to preserve quality. By understanding these dynamics, project leaders can make informed decisions to guide their projects towards successful completion.
Benefits of using the project management triangle
Implementing the project management triangle offers several significant advantages for project teams and stakeholders. Let’s explore these benefits in detail.
Easier change management
The triangle model facilitates effective change management. When changes occur, project managers can quickly assess their impact on scope, time, and cost. This allows for rapid evaluation of change requests, clear understanding of ripple effects and informed decision-making on adjustments.
Priority clarification
By visualising the three constraints, the triangle helps in clarifying priorities. Teams can identify critical project elements, focus resources on essential tasks and make trade-offs based on project goals.
Improved client communication
The project management triangle serves as a valuable communication tool. It enables project managers to explain project constraints clearly to clients, demonstrate the impact of changes visually and set realistic expectations for deliverables.
Risk reduction
Utilising the triangle model contributes to effective risk management. It helps teams anticipate potential issues early, develop contingency plans and balance risks across all three constraints.
By leveraging these benefits, project managers can navigate complex projects with greater confidence. The triangle model provides a structured approach to decision-making, ensuring that teams maintain focus on delivering quality outcomes while managing constraints effectively.
Managing the project management triangle
Effectively managing the project management triangle requires a strategic approach to balance scope, time, and cost while maintaining quality. Let’s explore key strategies to achieve this balance.
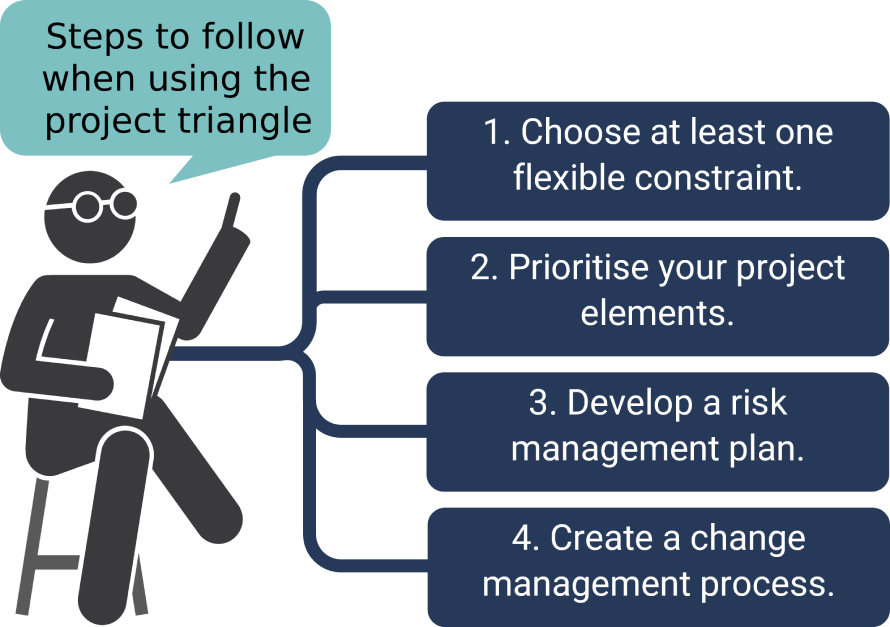
Choose at least one flexible constraint
Identifying a flexible constraint provides room for adjustments when challenges arise. Consider:
- Which constraint can be modified with minimal project impact?
- Are stakeholders open to adjusting scope, extending timelines, or increasing budget?
- How will flexibility in one area affect the other constraints?
By designating a flexible constraint, project managers can navigate unexpected issues more effectively.
Prioritise features and requirements
Carefully prioritising project elements helps maintain focus on critical deliverables. To do this:
- List all features and requirements
- Rank them based on importance and value
- Identify “must-haves” versus “nice-to-haves”.
This prioritisation enables informed decision-making when trade-offs become necessary.
Develop a risk management plan
A comprehensive risk management plan is crucial for maintaining balance within the triangle. Four steps include:
- Identify potential risks across all constraints
- Assess the likelihood and impact of each risk
- Develop mitigation strategies for high-priority risks
- Establish a monitoring system for ongoing risk assessment.
Proactive risk management helps prevent constraint imbalances before they occur.
Create a change management plan
Change is inevitable in projects. A robust change management plan helps maintain triangle equilibrium. Key components include:
- Clear processes for submitting and evaluating change requests
- Impact assessment procedures for each constraint
- Approval hierarchy for different types of changes
- Communication protocols for implemented changes.
A well-structured change management plan ensures that modifications don’t disrupt the project’s balance.
Match management methodology to priority constraints
Selecting an appropriate project management methodology can significantly impact triangle management. Consider these approaches:
- Waterfall, it is best for projects with fixed scope and sequential tasks. It emphasises detailed planning and documentation and suitable when time and cost are more flexible.
- Agile, it is ideal for projects requiring flexibility in scope. It focuses on iterative development and frequent feedback and adaptable to changing priorities and requirements.
- Lean, it emphasises efficiency and waste reduction. It prioritises cost management and value delivery and it is also suitable for projects with tight budget constraints.
Selecting the right methodology aligns with your project’s priorities and constraints.
By implementing these strategies, project managers can effectively balance the project management triangle. Remember, successful management requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. Regularly assess the balance between scope, time, and cost to ensure your project remains on track for success. Be prepared to make informed decisions and communicate changes clearly to all stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
Strategies for balancing constraints
Effectively managing the project management triangle requires a nuanced approach to each constraint. Let’s explore strategies for balancing scope, time, cost, and quality.
Scope management techniques
To maintain control over project scope, consider these techniques:
- Clear definition: Establish precise project boundaries and deliverables from the outset.
- Change control: Implement a formal process for evaluating and approving scope changes.
- Scope creep prevention: Regularly review project requirements against the original plan.
- Prioritisation: Use techniques like MoSCoW (Must, Should, Could, Won’t) to rank features.
Time management approaches
Efficient time management is crucial for project success. Consider these strategies:
- Critical path analysis: Identify and prioritise tasks that directly impact project completion.
- Resource levelling: Optimise resource allocation to prevent bottlenecks and delays.
- Time boxing: Allocate fixed time periods for specific tasks or project phases.
- Agile sprints: Break the project into short, focused work periods with defined goals.
Cost control methods
Maintaining budget integrity requires vigilant cost management. Implement these methods:
- Earned value management: Track project progress against budget and schedule baselines.
- Cost baseline: Establish a detailed budget breakdown for each project phase.
- Regular forecasting: Predict future costs based on current trends and performance.
- Vendor management: Negotiate favourable terms and monitor supplier costs closely.
Quality assurance practices
Balancing constraints should not compromise quality. Employ these practices:
- Quality standards: Define clear, measurable quality criteria for project deliverables.
- Continuous testing: Implement ongoing quality checks throughout the project lifecycle.
- Peer reviews: Utilise team expertise to identify and address quality issues early.
- Customer feedback: Regularly solicit and incorporate stakeholder input on deliverables.
By applying these strategies, project managers can effectively balance the competing demands of scope, time, cost, and quality. Remember, successful constraint management requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation to changing project conditions.
Tools for managing the project management triangle
Effective management of the project triangle often requires robust software solutions. Let’s explore some popular options and key features to consider.
Project management software options
- Monday.com is a versatile platform suitable for various project types. It is Visual boards for easy task tracking and prioritisation, and it also has customisable workflows to match specific project needs.
- ClickUp is a comprehensive tool with strong Agile project support. It has a time tracking and resource management features and also with multiple view options (list, board, Gantt, calendar).
- Teamwork is a client-focused platform with collaborative features. It has a budget and expense tracking capabilities and also has risk management and issue tracking tools.
Key features to look for in project management tools
When selecting a tool, prioritise these essential features:
- Constraint tracking: Ability to monitor scope, time, and cost simultaneously
- Resource allocation: Tools for optimising team and asset utilisation
- Reporting and analytics: Dashboards for real-time project status insights
- Collaboration features: Shared workspaces, communication tools, and file sharing
- Integration capabilities: Compatibility with other business software
- Customisation options: Flexibility to adapt to specific project methodologies
- Mobile accessibility: On-the-go project management for team members.
By leveraging these tools and features, project managers can more effectively balance the constraints of the project management triangle. The right software solution enhances visibility, improves communication, and facilitates data-driven decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Common challenges and solutions
Scope creep
Scope creep occurs when project requirements expand beyond the original plan. This can strain resources and timelines.
Solutions
- Implement a robust change control process
- Clearly define project boundaries in the initial planning phase
- Regularly review and communicate project scope with stakeholders
- Use a prioritisation system to evaluate new requests.
Time constraints
Tight deadlines can lead to rushed work and increased stress on the team.
Solutions
- Utilise critical path analysis to focus on essential tasks
- Implement time-boxing techniques to improve productivity
- Consider parallel task execution where possible
- Negotiate deadline extensions when necessary.
Budget limitations
Financial constraints can restrict resources and impact project quality.
Solutions
- Conduct thorough cost estimation during the planning phase
- Implement earned value management for better cost control
- Explore cost-effective alternatives for expensive resources
- Prioritise budget allocation based on critical project elements.
Balancing constraints may sometimes lead to quality issues in deliverables.
Solutions
- Establish clear quality standards at the project’s outset
- Implement regular quality checks throughout the project lifecycle
- Engage in continuous stakeholder feedback to ensure satisfaction
- Allocate adequate resources for testing and quality assurance.
By anticipating these challenges and preparing appropriate solutions, project managers can navigate the complexities of the project management triangle more effectively. Remember, successful project management often requires flexibility and creative problem-solving. Regularly assess your project’s status and be prepared to adapt your approach as needed to maintain the delicate balance between scope, time, cost, and quality.
Best practices for implementing the project management triangle
To effectively implement the project management triangle, consider these best practices:
Stakeholder communication
Clear communication is essential for managing expectations and maintaining alignment.
- Conduct regular stakeholder meetings to review project status
- Provide visual representations of the triangle to illustrate trade-offs
- Use plain language to explain technical concepts and constraints
- Encourage open dialogue to address concerns and gather feedback.
Regular monitoring and adjustments
Continuous oversight allows for timely interventions and course corrections.
- Implement a robust project tracking system
- Conduct frequent progress reviews against planned milestones
- Analyse variances in scope, time, and cost promptly
- Make data-driven decisions when adjusting project parameters.
Team collaboration and accountability
Foster a culture of shared responsibility for maintaining the triangle’s balance.
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities for each team member
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration to address challenges
- Implement a system for tracking individual and team performance
- Recognise and reward efforts that contribute to successful constraint management.
Continuous improvement
Embrace a mindset of ongoing refinement in your approach to the project triangle.
- Conduct post-project reviews to identify lessons learnt
- Analyse successful and unsuccessful strategies for balancing constraints
- Encourage team members to suggest process improvements
- Stay informed about new project management techniques and tools.
By incorporating these best practices, project managers can enhance their ability to navigate the complexities of the project management triangle. Remember, successful implementation requires commitment, adaptability, and a willingness to learn from both successes and setbacks
Applying the project management triangle
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into effective project management triangle application. Let’s explore three diverse case studies.
Large-scale IT project
A multinational corporation undertook a global ERP implementation. The project manager faced challenges balancing scope, time, and cost.
Key strategies include prioritised core functionalities to manage scope, implemented a phased rollout to control time and cost and utilised change management processes to evaluate new requirements.
Result: The project was completed within budget, with minimal timeline extension, and met all critical business needs.
Construction project
A commercial skyscraper construction project encountered unexpected geological challenges, threatening to disrupt the project triangle.
Key strategies include reallocated budget from non-essential features to address foundation issues, accelerated other construction phases to compensate for initial delays and negotiated with stakeholders to adjust project scope without compromising quality.
Result: The building was completed safely, with only a slight delay and minor budget increase.
Product development initiative
A tech startup aimed to launch a new software product in a competitive market, balancing innovation with time-to-market pressures.
Key strategies include employed Agile methodology to manage scope flexibly, focused on developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for initial release and utilised user feedback to prioritise post-launch feature development.
Result: The product launched on time, within budget, and quickly gained market share due to its core functionality and subsequent iterative improvements.
These case studies demonstrate how effective management of the project triangle can lead to successful outcomes across various industries and project types. By carefully balancing scope, time, and cost constraints, project managers can navigate complex challenges and deliver value to stakeholders.
Conclusion
The project management triangle serves as a crucial framework for balancing scope, time, and cost in project execution. By understanding and applying this concept, project managers can effectively manage project constraints, make informed decisions when trade-offs are necessary and maintain focus on delivering high-quality outcomes
Remember that successful project management requires clear communication with stakeholders, regular monitoring and adjustment of project parameters, team collaboration and accountability and continuous improvement of processes
Balancing these constraints is essential for project success across various industries and project types. As demonstrated in the case studies, effective application of the project management triangle can lead to remarkable results.
We encourage you to implement these principles in your projects. By doing so, you’ll be better equipped to navigate challenges, meet stakeholder expectations, and consistently deliver successful outcomes. Embrace the project management triangle as a valuable tool in your project management toolkit.
FAQs
What is the iron triangle in project management?
The iron triangle is another term for the project management triangle, emphasising the balance between scope, time, and cost.
How does changing one constraint affect the others in the project management triangle?
Altering one constraint typically requires adjustments to one or both of the others to maintain balance and quality.
Can the project management triangle be applied to all types of projects?
Yes, the concept is versatile and applicable across various industries and project types.
What are some signs that a project’s constraints are out of balance?
Frequent scope changes, missed deadlines, budget overruns, or quality issues may indicate imbalanced constraints.
How often should project managers review and adjust the project management triangle?
Regular reviews are essential, typically at key milestones or when significant changes occur.
What role does innovation play in managing the project management triangle?
Innovation can help optimise processes, potentially allowing for improvements across all constraints simultaneously.
Infographic