Introduction
In today’s business environment, project management skills are more crucial than ever. Organisations increasingly rely on skilled professionals to guide complex initiatives to successful completion. The demand for competent project managers continues to grow across industries, with employers seeking individuals who possess a diverse set of abilities.
Effective project management requires a blend of:
- Technical expertise
- Leadership qualities
- Business acumen.
These skills enable managers to:
- Plan and execute projects efficiently
- Lead teams effectively
- Align initiatives with organisational goals.
As the business landscape evolves, so do the competencies required for project success. This article explores the essential project management skills needed to thrive in modern workplaces. By mastering these capabilities, professionals can position themselves for rewarding careers and drive significant value for their organisations.
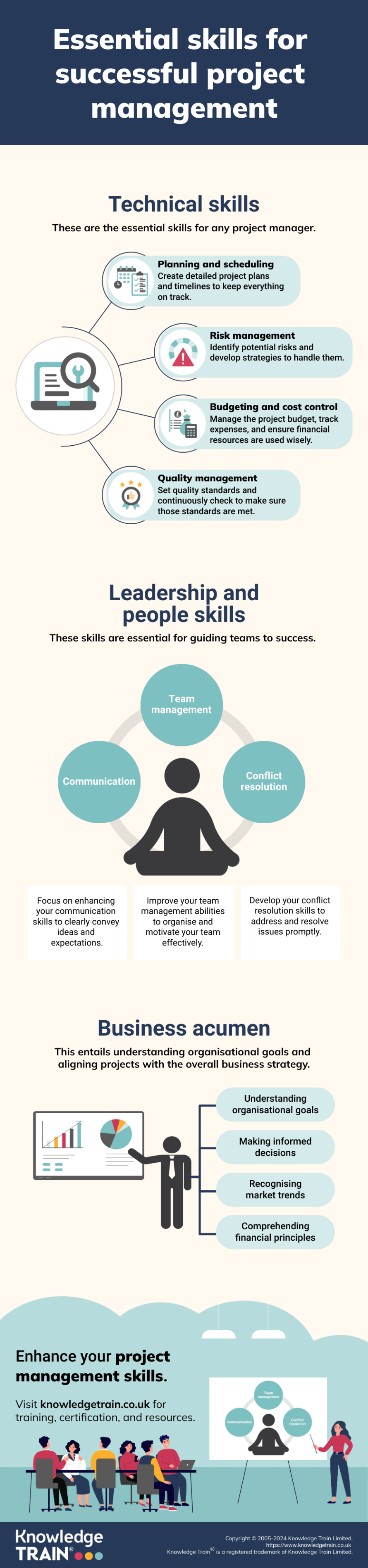
Technical project management skills
Mastering technical project management skills is essential for delivering successful projects. These competencies form the foundation of effective project execution and control.
Planning and scheduling
Creating comprehensive project plans
Project plans are crucial for guiding initiatives from inception to completion. A well-crafted plan should include:
- Clear project objectives
- Detailed scope definition
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Resource allocation
- Milestones and deliverables.
Utilise project management approaches like Agile or waterfall to structure your plans effectively.
Effective time management techniques
Efficient time management ensures projects stay on track. Consider implementing these techniques:
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Gantt charts for visual scheduling
- Time-boxing for task completion
- Regular progress tracking and reporting.
Risk management
Identifying potential risks
Proactive risk identification is crucial for project success. Employ methods such as:
- SWOT analysis
- Brainstorming sessions with team members
- Historical data review from similar projects
- Expert interviews.
Developing mitigation strategies
Once risks are identified, develop strategies to address them:
- Avoidance: Eliminate the threat entirely
- Mitigation: Reduce the likelihood or impact
- Transfer: Shift the risk to a third party
- Acceptance: Acknowledge and monitor the risk
Budgeting and cost control
Creating and managing project budgets
Accurate budgeting is vital for financial success. Consider these steps:
- Estimate costs for each project component
- Include contingency funds for unforeseen expenses
- Obtain stakeholder approval for the budget
- Establish a baseline for future comparisons
Monitoring and controlling expenses
Regularly track expenses to ensure adherence to the budget:
- Implement Earned Value Management (EVM)
- Conduct periodic cost reviews
- Use project management software for real-time tracking
- Address variances promptly to prevent overruns.
Quality management
Implementing quality assurance processes
Ensure project deliverables meet required standards through:
- Establishing clear quality metrics
- Conducting regular quality audits
- Implementing peer reviews and inspections
- Utilising quality control tools (e.g., Pareto charts, control charts).
Continuous improvement strategies
Foster a culture of ongoing enhancement:
- Conduct post-project reviews
- Encourage team feedback and lessons learned
- Implement process improvements based on insights gained
- Stay updated on industry best practices.
By honing these technical project management skills, professionals can significantly improve their ability to deliver projects successfully.
Leadership and interpersonal skills
Effective project management extends beyond technical expertise. Strong leadership and interpersonal skills are crucial for guiding teams and ensuring project success.
Communication
Verbal and written communication techniques
Clear communication is the cornerstone of project management. Enhance your skills by:
- Tailoring your message to your audience
- Using concise language and avoiding jargon
- Employing visual aids to reinforce key points
- Practising public speaking and presentation skills.
Active listening and feedback
Effective communication is a two-way process. Improve your listening skills by:
- Focusing on the speaker without interruption
- Asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding
- Summarising key points to confirm comprehension
- Providing constructive feedback in a timely manner.
Team management
Delegation and task assignment
Proper delegation is essential for efficient project execution:
- Assess team members’ strengths and weaknesses
- Match tasks to individual skills and experience
- Provide clear instructions and expectations
- Establish accountability and follow-up mechanisms.
Motivating and inspiring team members
Foster a positive team environment to enhance productivity:
- Recognise and celebrate individual and team achievements
- Provide opportunities for professional growth and development
- Encourage open communication and idea-sharing
- Lead by example, demonstrating enthusiasm and commitment.
Conflict resolution
Identifying and addressing conflicts
Proactively manage conflicts to maintain team harmony:
- Recognise early warning signs of disagreements
- Address issues promptly and directly
- Encourage open dialogue between conflicting parties
- Remain impartial and focus on finding solutions.
Negotiation and mediation techniques
Develop skills to facilitate resolutions:
- Practice active listening to understand all perspectives
- Identify common ground and shared interests
- Propose creative solutions that benefit all parties
- Seek win-win outcomes whenever possible.
Conflict resolution
Identifying and engaging stakeholders
Effective stakeholder management is critical for project success:
- Conduct a thorough stakeholder analysis
- Develop a stakeholder engagement plan
- Establish regular communication channels
- Involve key stakeholders in decision-making processes.
Managing expectations and relationships
Build and maintain positive stakeholder relationships:
- Clearly communicate project goals, timelines, and constraints
- Provide regular updates on project progress and challenges
- Address concerns and issues promptly
- Seek feedback and incorporate valuable suggestions.
By developing these leadership and interpersonal skills, project managers can create a positive team environment, foster collaboration, and drive project success through effective communication and relationship management.
Business acumen and strategic thinking
Successful project managers possess a strong understanding of business principles and strategic thinking. These skills enable them to align projects with organisational goals and drive value.
Understanding organisational goals and objectives
To effectively contribute to an organisation’s success, project managers should:
- Familiarise themselves with the company’s mission and vision
- Stay informed about industry trends and market conditions
- Understand the organisation’s competitive landscape
- Regularly review financial reports and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Aligning projects with business strategy
Strategic alignment ensures that projects support overarching business objectives:
- Identify how each project contributes to strategic goals
- Prioritise projects based on their strategic importance
- Communicate the strategic value of projects to stakeholders
- Adjust project plans as business strategies evolve.
Decision-making and problem-solving
Effective project managers make informed decisions and solve complex problems:
- Gather and analyse relevant data before making decisions
- Consider multiple alternatives and their potential consequences
- Use structured problem-solving techniques (e.g., root cause analysis)
- Balance short-term needs with long-term strategic objectives.
Adaptability and change management
In today’s dynamic business environment, adaptability is crucial:
- Anticipate and prepare for potential changes in the business landscape
- Develop contingency plans for various scenarios
- Foster a culture of flexibility and innovation within project teams
- Implement change management strategies to support organisational transitions.
By cultivating business acumen and strategic thinking skills, project managers can:
- Make better-informed decisions
- Align projects more effectively with organisational goals
- Adapt to changing business conditions
- Drive meaningful value for their organisations.
These competencies elevate project managers from tactical executors to strategic partners, enhancing their ability to contribute to overall business success.
Technical proficiency
In today’s digital age, project managers must possess strong technical skills to effectively manage projects and teams.
Project management software and tools
Popular project management software options
Familiarise yourself with popular industry tools such as:
- Microsoft Project: Comprehensive planning and scheduling
- Jira: Agile project management and issue tracking
- Trello: Visual task management using boards and cards
- Asana: Team collaboration and workflow management.
Collaboration and communication tools
- Slack: Real-time messaging and file sharing
- Microsoft Teams: Video conferencing and document collaboration
- Zoom: Virtual meetings and webinars
- Google Workspace: Cloud-based document creation and sharing.
Data analysis and reporting
Creating and interpreting project reports
Develop proficiency in:
- Generating status reports using project management software
- Creating visual representations of data (e.g., charts, graphs)
- Customising reports for different stakeholders
- Interpreting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics.
Creating and interpreting project reports
Leverage data to inform project decisions:
- Collect and analyse project performance data
- Use statistical tools to identify trends and patterns
- Employ predictive analytics for risk assessment
- Present data-driven recommendations to stakeholders.
By mastering these technical skills, project managers can streamline processes, improve communication, and make informed decisions based on accurate data analysis.
Developing your project management skills
Enhancing your project management capabilities is an ongoing process. Consider the following approaches to expand your skillset:
Formal education and training
Pursue advanced degrees or specialised courses in project management:
- Master’s degree in project management
- Short courses or workshops on specific methodologies (e.g., Agile, PRINCE2)
- Online learning platforms like GainCert.
Professional certifications
Obtain industry-recognised certifications to validate your expertise:
- Project Management Professional (PMP) from PMI
- PRINCE2 Practitioner
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM).
On-the-job experience and mentoring
Practical experience is invaluable for skill development:
- Seek challenging project assignments
- Learn from experienced colleagues
- Participate in cross-functional projects
- Find a mentor to guide your professional growth.
Continuous learning and self-improvement
Stay current with industry trends and best practices:
- Read project management publications and blogs
- Attend conferences and networking events
- Join professional associations (e.g., PMI, APM)
- Reflect on past projects and identify areas for improvement
By combining these approaches, you can continuously enhance your project management skills and advance your career in this dynamic field.
Conclusion
Mastering essential project management skills is crucial for success in today’s competitive business environment. Effective project managers combine:
- Technical expertise
- Leadership abilities
- Business acumen
- Interpersonal skills.
By integrating these competencies, professionals can deliver projects that drive organisational value. The journey to becoming an exceptional project manager requires continuous learning and development. Embrace opportunities to enhance your skills through:
- Formal education
- Professional certifications
- Practical experience
- Self-improvement initiatives.
As you refine your project management capabilities, you’ll be well-positioned to tackle complex challenges and lead teams to success. Commit to ongoing skill development to thrive in this dynamic field.
FAQs
What are the most important skills for a project manager?
Key project management skills include:
- Communication
- Leadership
- Planning and organisation
- Risk management
- Problem-solving
- Technical proficiency
- Adaptability.
A combination of these skills enables project managers to lead teams effectively and deliver successful projects.
How can I improve my project management skills?
To enhance your project management capabilities:
- Pursue formal education or training
- Obtain professional certifications
- Seek mentorship from experienced project managers
- Take on challenging projects to gain practical experience
- Stay updated on industry trends and best practices
- Continuously reflect on and learn from your experiences.
What software tools are essential for project managers?
Essential project management tools include:
- Planning and scheduling software (e.g., Microsoft Project, Primavera)
- Collaboration platforms (e.g., Slack, Microsoft Teams)
- Task management tools (e.g., Trello, Asana)
- Data analysis and reporting software (e.g., Excel, Power BI).
The specific tools required may vary depending on the project and organisation.
How do project management skills differ across industries?
While core project management skills are transferable, industry-specific knowledge is often required. For example:
- IT projects may require expertise in Agile methodologies
- Construction projects often emphasise cost and resource management
- Healthcare projects may focus on regulatory compliance and patient safety
Adapting your skills to the specific needs of each industry is crucial for success.
What certifications are valuable for project managers?
Valuable project management certifications include:
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- PRINCE2 Practitioner
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM)
- Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)
- ITIL Foundation.
Choose certifications that align with your career goals and industry requirements.
Infographic