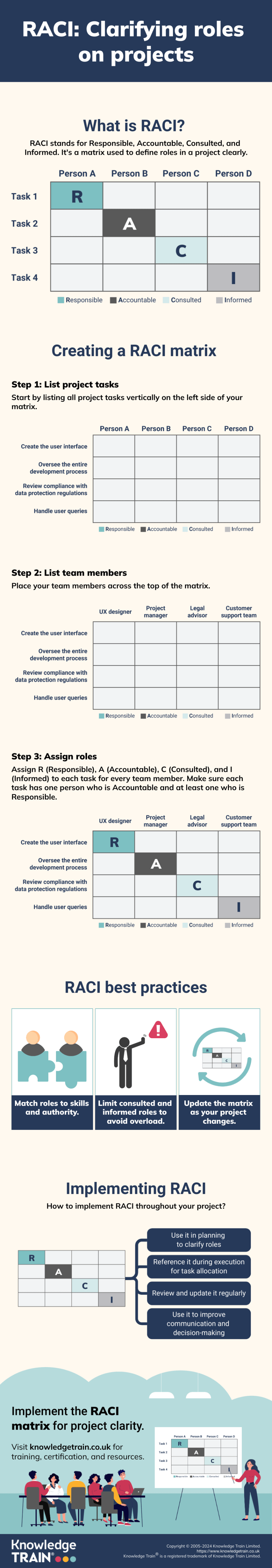
RACI matrix in project management
Key takeaways
A RACI matrix clarifies who does the work, who signs it off, and who needs input or updates.
- Use RACI to reduce role confusion, duplicated effort, and slow decisions on cross-functional projects.
- Ensure every task has at least one Responsible character and exactly one Accountable character.
- Limit Consulted and Informed assignments to avoid information overload and meeting sprawl.
- Validate the chart with stakeholders, then keep it visible and updated as the project changes.
- Adapt the model when needed, such as RASCI or DACI, and align it to lifecycle phases and Agile ceremonies.

Introduction
Project management is all about getting things done with clarity and efficiency. That’s where the RACI matrix comes in: an effective tool that helps define roles and responsibilities on your projects. It is also called a responsibility assignment chart.
The RACI matrix is based on a simple but powerful acronym: RACI. Each letter represents a different role in a project task or deliverable and spelling them out across a table is an easy way to ensure that everyone involved knows who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed for each aspect of the work. Clear RACI definitions drive better communication and more streamlined decision-making.
RACI is an important tool for project management as it brings clarity to who oversees what on your projects, so it is crucial to understand and make the most of this framework. With RACI, you can say goodbye to uncertainty about who owns a task or deliverable, disputes and delays over work that may or may not have been delegated, poor team collaboration, or failure to include the right people and at the right level on key decisions.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about the RACI matrix, including how to create one, how to apply it in project management, and how to adapt it to the specific needs of your organisation. We will also discuss the benefits and limitations of the matrix and show you real-life examples to get you started. By the end of the article, you will have the knowledge and skills you need to use RACI as a project manager.
Understanding the RACI matrix
A RACI matrix is a chart that maps out roles and responsibilities for your projects and teams. It is based on a simple acronym: RACI, which stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. RACI as a framework is also sometimes known as the responsibility assignment matrix or RAM.
What does each letter stand for in RACI?
- Responsible: These are the people who actually do the work; they are the doers who are completing tasks and creating deliverables. For a task or deliverable, there can be one or more responsible people.
- Accountable: This person is ultimately answerable for the correct and timely completion of the task or deliverable. It is the only one who approves the work of the responsible people. For a task or deliverable, there can be one and only one accountable person.
- Consulted: These stakeholders have a role in providing information, inputs, or advice for the task or deliverable; they are consulted or actively involved in the discussion. But they are not the ones who do the work. For a task or deliverable, there can be one or more consulted people.
- Informed: These people need to be kept updated on progress and developments for the task or deliverable; they do not have a direct contribution but must be notified of outcomes or major decisions.
The main goal of RACI matrix is to improve project efficiency and communication. Here are some of the benefits of using RACI matrix:
- Defining roles
- Better accountability
- Smooth decision-making
- Minimising conflicts and duplications
- Optimising resource allocation.
You can effectively use RACI matrix in the following situations:
- Projects with many stakeholders
- Cross-functional teams working together
- Unclear or overlapping roles/responsibilities
- Organisational change or restructuring
- New team formation. Assigning a Responsible person.
In practice, the RACI matrix helps project managers to clearly assign each task to one or more Responsible persons. This helps to avoid confusion and ensure that everyone knows who is doing what. The matrix also helps in stakeholder engagement by identifying who needs to be consulted or informed at each stage of the project.
The RACI matrix is not always required, for example, for small and short-term projects or projects with a small team of stakeholders. In such cases, communication and coordination can be achieved in a less formal way. However, for most projects of medium and larger size, the use of a RACI matrix is a simple and effective way to organise work and improve communication.
Creating a RACI matrix
Six steps guide to building a RACI chart
The following are the steps to create a RACI matrix:
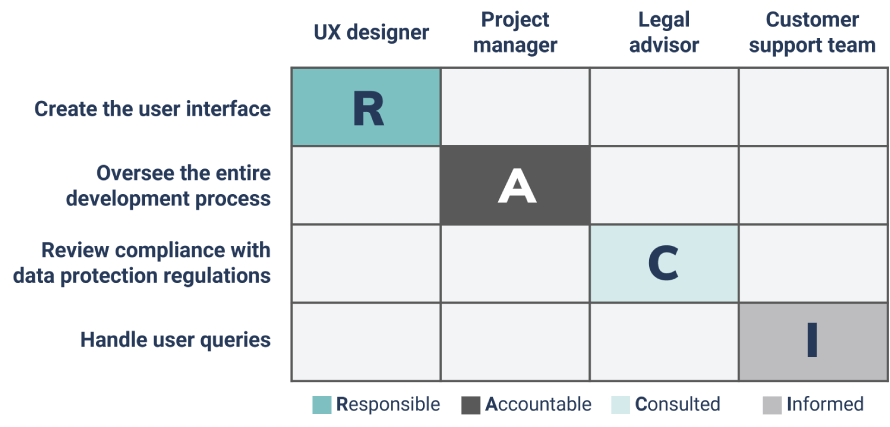
- Identify the tasks: List all the tasks and milestones of the project in the left column of the RACI matrix.
- Define the stakeholders: List all the project stakeholders in the top row of the matrix.
- Assign the roles: For each task, assign one of the four roles (R, A, C, I) to each stakeholder.
- Review and refine: Check that each task has at least one R and one A, and that there are no conflicts or ambiguities in the assignments.
- Validate: Confirm the RACI matrix with the team members and stakeholders to ensure accuracy and agreement.
- Distribute: Share the RACI matrix with all the stakeholders and make it accessible for reference and updates.
Best practices for assigning roles
The following are some tips for assigning roles in a RACI matrix:
- Make sure that all the team members understand the RACI definitions and agree on the roles.
- Assign roles based on the skills, authority, and availability of the team members, and not just on their positions.
- Avoid assigning too many Consulted and Informed roles, as this can lead to information overload and unnecessary communication.
- Consider the scope and complexity of the project when defining the tasks and assigning the roles.
- Update the RACI matrix as the project progresses or as changes occur in the team or the tasks.
Common mistakes to avoid
The following are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a RACI matrix:
- Including too many tasks or too many stakeholders: Focus on the most important tasks and stakeholders and avoid unnecessary details.
- Assigning multiple Rs or As to the same task: This can create confusion and conflict over responsibility. Ensure that each task has one and only one A and at least one R.
- Not getting buy-in from the stakeholders: Ensure that all the stakeholders agree on the roles and responsibilities assigned to them or to others.
- Not updating the RACI matrix: The RACI matrix should be a living document, not a static one. Review and update it as needed.
- Not using the RACI matrix consistently: Ensure that all the team members use the RACI matrix as a reference and respect the roles and responsibilities assigned.
RACI matrix templates and tools
A RACI matrix can be created using different tools and templates. Here are some of them:
- Spreadsheet software: You can use a simple Excel or Google Sheets template to create a RACI matrix, which allows you to customise and format the chart.
- Project management software: Many project management tools, such as Monday.com, offer built-in RACI matrix features, which allow you to create, share, and update the matrix along with other project elements.
- RACI matrix software: There are some specialised software that focus on creating and managing RACI matrices, which offer advanced features and integrations.
- Visual collaboration tools: There are some visual collaboration platforms, such as Miro, which offer interactive RACI matrix templates, which allow you to create and collaborate on the matrix visually.
Choose the tool that best suits your team’s needs and preferences, and that integrates well with your existing project management processes. Remember that a RACI matrix is only as good as its clarity and consistency, so make sure that you use it correctly and regularly.
Implementing RACI in project management

Integrating RACI with project lifecycles
To effectively integrate RACI into your project management approach, align it with the project lifecycle phases. Here’s how you can do it:
- Initiation: Identify key stakeholders and establish their high-level RACI roles for the project.
- Planning: Develop a detailed RACI matrix for all identified tasks and deliverables.
- Execution: Apply the RACI matrix to allocate tasks, facilitate communication, and ensure accountability.
- Monitoring: Continuously review and update RACI assignments as needed throughout the project.
- Closing: Evaluate the effectiveness of RACI for lessons learned and future projects.
Using RACI to enhance communication
RACI charts establish clear lines of communication by identifying who needs what information and when, Minimising unnecessary meetings and emails, clarifying decision-making processes, and ensuring all relevant parties are consulted.
Ask team members to consult the RACI matrix when sending updates or requesting input.
Resolving conflicts and ambiguities in RACI assignments
Facilitate discussions to resolve conflicts by reviewing the project scope and objectives, clarifying role definitions and expectations, considering team members’ skills and workloads, making necessary adjustments to balance responsibilities, and documenting and communicating any changes.
Team members should have regular discussions about their RACI roles to avoid misunderstandings and encourage collaboration.
RACI and Agile project management
Although RACI is a common tool in the traditional project management, it can be adapted and integrated with Agile methodologies as well. Here are some tips on how to do that:
- Use RACI for high-level project roles and responsibilities
- Adapt RACI for each sprint or iteration
- Focus on team roles instead of individual assignments
- Incorporate RACI discussions into sprint planning and retrospectives.
In Scrum, RACI can be used to define roles and responsibilities for each Scrum ceremony, epic, and user story. For example:
- A Product Owner is Accountable for prioritising and approving the product backlog items.
- A Scrum Master is Responsible for facilitating the Scrum process and addressing impediments.
- The Development Team is Responsible for delivering potentially shippable product increments.
By using RACI in Scrum, teams can achieve a balance between structure and flexibility.
RACI matrix variations and alternatives
In addition to the standard RACI matrix, there are several variations and alternatives that can be used for specific project needs. Here are a few examples:
RASCI (adding the ‘supportive’ role)
- Supportive: People who support the Responsible person in completing the task.
This could be useful for projects that have resource needs and specialist help.
CARS (Communicate, Approve, Responsible, Support)
CARS is a simplified version of RACI that uses only four roles:
- Communicate: Similar to Informed in RACI
- Approve: Equivalent to Accountable
- Responsible: Same as in RACI
- Support: Combines Consulted and Supportive roles.
This can help making communication and approval fast and efficient.
DACI (Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed)
DACI is an alternative to RACI that focuses on decision-making:
- Driver: The person in charge of driving the initiative forward (similar to Responsible)
- Approver: The person who has the final decision-making authority (similar to Accountable)
- Contributor: The people who provide input and expertise (similar to Consulted)
- Informed: Same as in RACI.
DACI works well for projects where decision-making is complicated.
Choosing the right model for your project
When choosing a RACI matrix model for your project, there are several factors to consider. Here are some key ones:
- The complexity and size of the project
- The structure and culture of the team
- The decision-making processes in place
- The communication needs and preferences
- The level of involvement of the stakeholders.
The key is to select the model that best fits your project requirements and helps to optimise clarity and efficiency.
Benefits and limitations of RACI
Advantages of using RACI in project management
RACI matrices provide several benefits for project management, including:
- Clarity: Establishes clear roles and responsibilities for each task in a project
- Accountability: Ensures that each task has an assigned responsible person
- Efficiency: Reduces duplication of work and confusion by defining roles
- Communication: Facilitates better information flow among team members
- Conflict resolution: Provides a framework for addressing role-related conflicts
- Workload management: Identifies potential overloading of team members with multiple responsibilities.
These advantages make RACI matrices a valuable tool for smooth project execution and improved team performance.
Potential drawbacks and challenges
While RACI offers many benefits, some potential drawbacks and challenges may include:
- Time-consuming: Creating and maintaining RACI matrices can be labor-intensive and time-consuming
- Oversimplification: RACI may oversimplify complex projects and not capture all nuances
- Rigidity: The RACI framework can be rigid, leading to a lack of flexibility if not regularly updated
- Misinterpretation: Team members may misinterpret their assigned roles in the matrix
- Resistance: Some team members may resist the structured approach of RACI
Overcoming RACI implementation obstacles
To overcome these challenges and limitations of RACI, project managers can:
- Utilise project management software to automate the creation and maintenance of RACI matrices
- Regularly review and update the RACI matrix to adapt to project changes
- Provide comprehensive training to team members on RACI concepts and implementation
- Encourage open communication and feedback regarding role assignments in the matrix
- Customise and adapt the RACI framework to fit the unique needs and culture of the organisation
- Start with smaller projects to gain familiarity and acceptance of the RACI approach before implementing it on larger scales
Addressing these potential limitations proactively can help maximise the benefits of RACI while minimising its drawbacks. It’s important to remember that RACI is a project management tool that aids in coordination, not a rigid set of rules to be strictly followed.
Case studies and real-world applications
Success stories of RACI implementation
Some examples of organisations that have successfully implemented RACI:
- A multinational technology company implemented RACI to streamline a complex software development project. The result was a 30% reduction in project delays.
- A healthcare provider applied RACI to enhance patient care coordination. Patient satisfaction scores increased by 25% as a result.
- A government agency used RACI for policy development, leading to a 40% decrease in decision-making time.
Lessons learned from RACI failures
Conversely, here are some instances where RACI implementation faced challenges:
- A manufacturing firm experienced difficulties with RACI due to insufficient staff training, resulting in role confusion and project delays.
- A financial services company created an overly complicated RACI matrix. The excessive detail became more of a hindrance than a help, slowing down project progress.
- An educational institution did not regularly update their RACI matrix. This led to outdated role assignments and communication breakdowns.
These case studies emphasise the importance of proper training, avoiding over-complication, and regularly updating the RACI matrix during its implementation.
Conclusion
The RACI matrix is an effective project management tool that promotes clarity, accountability, and efficiency. By assigning roles and responsibilities, it helps to streamline communication and decision-making processes. We encourage project managers to leverage RACI in their projects, adapting it to their unique requirements for enhanced project success and team collaboration.
FAQs
What is the difference between ‘Responsible’ and ‘Accountable’ in a RACI matrix?
In a RACI matrix, the individual or individuals who do the task are marked as Responsible. On the other hand, the person who is ultimately answerable for the task’s completion is marked as Accountable. This means that the Accountable person must sign off on the work of the Responsible parties, and is often the one who delegates the work.
How often should a RACI matrix be updated during a project?
A RACI matrix should be updated whenever there are significant changes to the project team or the project itself. This may include changes in team members, tasks, or the overall scope of the project. Additionally, it’s a good practice to review the RACI matrix at regular intervals, such as monthly, to ensure it’s still accurate.
Can a RACI matrix be used for small projects or teams?
Yes, a RACI matrix can be used for any project or team size. It’s particularly helpful for small teams or projects, as it clearly defines roles and responsibilities, which can sometimes be overlooked or become unclear in smaller settings. For smaller projects, a simplified RACI matrix may be appropriate.
What are the key indicators that a project needs a RACI matrix?
The key indicators that a project might benefit from a RACI matrix include: role confusion, unclear decision making processes, involvement of multiple departments or teams, overlapping responsibilities among team members, and frequent communication breakdowns.
How does RACI differ from other project management tools like Gantt charts?
RACI and Gantt charts serve different purposes. While a Gantt chart visually represents the project schedule, a RACI matrix clarifies roles and responsibilities for each task. They can be used together for more effective project management.
Is it possible to have multiple people ‘Responsible’ for a single task?
Yes, multiple people can be assigned the ‘Responsible’ role for a task. However, it’s important to ensure there’s a clear division of work to prevent confusion or duplication of effort.
How can I introduce RACI to a team that’s resistant to change?
Introducing RACI to a resistant team can be a challenge. Start by clearly communicating the benefits of RACI, emphasising how it can streamline work and reduce misunderstandings. Implement RACI gradually, perhaps on a small project or task, to demonstrate its value without overwhelming the team. Involve the team in creating the RACI matrix. This gives them a sense of ownership and allows them to provide input. Provide adequate training and support to ensure everyone understands the system. Once the team sees the benefits of RACI, resistance should decrease.
What software or tools are best for creating and managing RACI matrices?
There are several software and tools that can be used to create and manage RACI matrices. These include spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, project management platforms like Asana or Trello, or dedicated RACI tools like TeamGantt or Lucidchart. The best tool depends on your specific needs and the software your team is already using.
How does RACI fit into Agile project management methodologies?
RACI can complement Agile methodologies by providing clarity on roles within Agile teams, such as during sprints. The roles in RACI can be adapted to fit the Agile environment, focusing on team roles rather than individual assignments.
Can RACI be used across different departments or only within a single team?
RACI can be used both within teams and across different departments or functions. It’s especially useful for projects that involve multiple departments, as it can help clarify roles and responsibilities across different areas of the organisation.
Infographic