Introduction
Project management is the systematic application of knowledge, skills, and techniques to achieve specific objectives within defined constraints. It’s a crucial discipline for organisations seeking to deliver value efficiently.
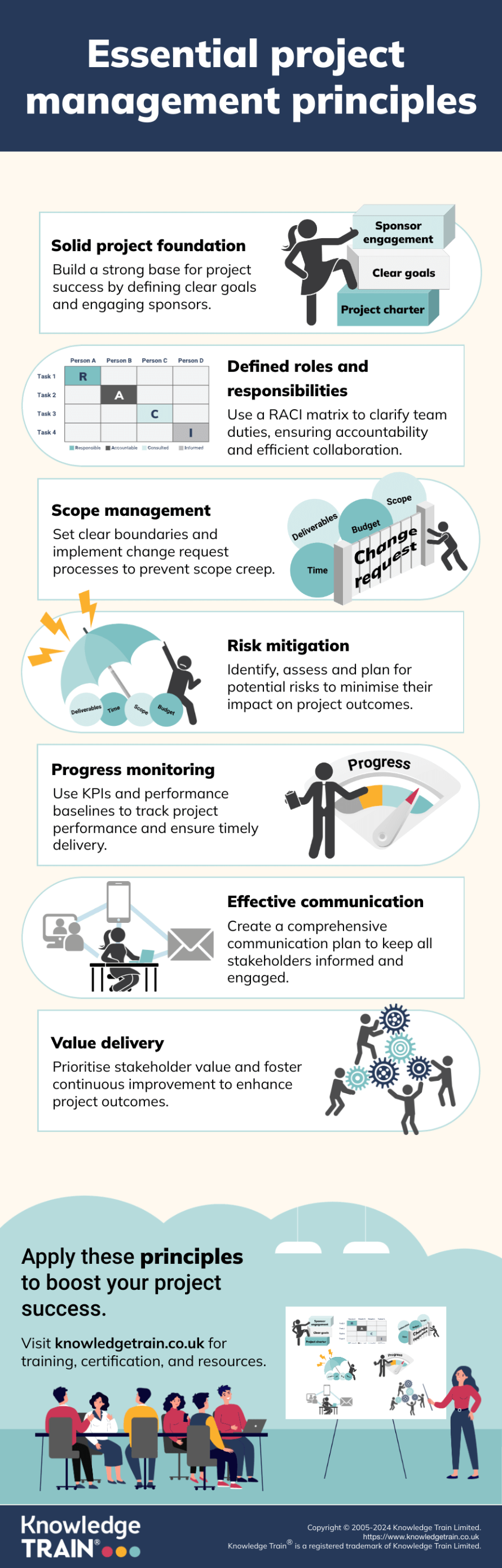
Project management principles serve as fundamental guidelines, ensuring consistent success across diverse industries and project types. These principles provide a framework for effective planning, execution, and control.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- Essential project management principles
- Strategies for implementing these principles
- Techniques for overcoming common challenges.
By understanding and applying these principles, project managers can significantly improve their project outcomes and deliver greater value to stakeholders. After reading this article, you might find it useful to learn about the PRINCE2 principles as described in this popular project management methodology.
Establishing a solid project foundation
A strong foundation is essential for project success. This section explores three key elements: formal structure, clear objectives, and sponsor engagement.
Formal project structure
A well-defined structure provides a framework for project execution:
- Project charter: Outlines project purpose, scope, and stakeholders
- Project plan: Details timelines, resources, and deliverables.
- Designated team: Assigns roles and responsibilities.
Clear goals and objectives
Precise requirements are crucial for project success:
- Importance: Clear goals prevent misunderstandings and scope creep
- Alignment: Ensure project objectives support broader company goals
- Documentation: Formally record and approve project criteria.
| Benefit | Description |
| Focus | Guides team efforts towards specific outcomes |
| Measurement | Provides benchmarks for assessing progress |
| Clarity | Reduces ambiguity in project execution |
Project sponsor engagement
An engaged sponsor can significantly impact project success:
- Role: Provides high-level support and guidance
- Benefits: Secures resources, removes obstacles, and champions the project
- Strategies: Regular updates, clear communication, and involvement in key decisions.
By establishing these essential elements, project managers create a solid base for successful project execution and delivery.
Defining roles and responsibilities
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are crucial for project success. This section explores team accountability and the project manager’s role.
Team accountability
Establishing accountability ensures each team member understands their duties and expectations.
RACI/RASCI matrix
The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) or RASCI (with Sign-off) matrix clarifies roles:
- Responsible: Who performs the task
- Accountable: Who oversees the task’s completion
- Consulted: Whose input is sought
- Informed: Who is kept updated
- Sign-off (RASCI only): Who approves the task.
Stakeholder register
A stakeholder registers documents key information about project stakeholders. It includes contact details, influence level, communication preferences and engagement strategy.
Project manager’s role
The project manager’s responsibilities are multifaceted and critical to project success.
Key responsibilities
- Planning and scheduling
- Resource allocation
- Risk management
- Budget oversight
- Quality assurance.
Leadership and communication skills
Effective project managers demonstrate:
- Clear communication
- Conflict resolution abilities
- Motivational techniques
- Adaptability to change
- Strategic thinking.
By clearly defining roles and fostering accountability, project teams can operate more efficiently and effectively.
Managing project scope and changes
Effective management of project scope and changes is essential for maintaining project integrity and success.
Scope creep prevention
Defining project boundaries
Clearly delineate project boundaries to prevent uncontrolled expansion. To achieve this, it is crucial to document specific project deliverables, identify exclusions explicitly and set measurable acceptance criteria.
Change management processes
Implement robust change control procedures:
- Formal change request submission
- Impact assessment (time, cost, resources)
- Stakeholder review and approval
- Documentation of approved changes.
Adaptability in project management
Flexibility in project lifecycle
Incorporate flexibility to accommodate necessary changes:
- Use iterative approaches when appropriate
- Conduct regular project reviews
- Maintain open communication channels.
Balancing change and stability
Strike a balance between adaptability and project stability:
| Aspect | Strategy |
| Scope | Prioritise changes based on value and impact |
| Schedule | Build buffer time into project timelines |
| Resources | Cross-train team members for versatility |
| Budget | Allocate contingency funds for unforeseen changes |
By effectively managing scope and changes, project managers can ensure projects remain on track while accommodating necessary adjustments. This balance promotes project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
Risk management and mitigation
Effective risk management is crucial for project success. This section explores methods for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks.
Identifying and assessing risks
Risk categories
Common risk categories include:
- Technical risks
- Financial risks
- Operational risks
- External risks (e.g., market, regulatory).
Risk assessment techniques
Employ these techniques to evaluate potential risks:
- Risk probability and impact matrix
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Delphi technique (expert consensus)
- Fault tree analysis.
Developing risk mitigation strategies
Preventive measures
Implement proactive strategies to minimise risk occurrence:
- Regular risk reviews
- Clear communication protocols
- Robust quality assurance processes
- Continuous staff training.
Contingency planning
Develop contingency plans for identified risks:
| Risk level | Action |
| Low | Monitor and reassess periodically |
| Medium | Develop specific response strategies |
| High | Create detailed action plans and allocate resources |
Effective risk management involves continuous monitoring and adaptation. By systematically addressing potential risks, project managers can enhance project resilience and increase the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Monitoring and measuring project progress
Effective monitoring and measurement are essential for ensuring project success. This section explores key performance indicators and performance management baselines.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Selecting appropriate KPIs
Choose KPIs that align with project objectives:
- Schedule performance index (SPI)
- Cost performance index (CPI)
- Quality metrics
- Stakeholder satisfaction scores.
Tracking and reporting methods
Implement robust tracking and reporting systems:
- Regular status meetings
- Automated dashboards
- Earned Value Management (EVM)
- Milestone tracking.
Performance management baseline
Integrating cost, schedule, and scope
Develop a comprehensive baseline incorporating:
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Project timeline
- Budget allocation.
| Element | Integration method |
| Cost | Map budget to WBS elements |
| Schedule | Link timeline to WBS deliverables |
| Scope | Align WBS with project objectives |
Using baselines for decision-making
Leverage baselines to:
- Identify variances early
- Forecast project outcomes
- Justify corrective actions
- Evaluate change requests.
By establishing clear KPIs and performance baselines, project managers can effectively monitor progress and make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
Effective communication and collaboration
Communication and collaboration are vital for project success. This section explores strategies for developing communication plans and leveraging collaboration tools.
Communication plan development
Stakeholder communication needs
Identify and address diverse stakeholder requirements:
- Executive sponsors: High-level updates
- Team members: Detailed task information
- Clients: Progress reports and milestones
- External partners: Relevant project aspects.
Communication channels and frequency
Establish appropriate channels and cadence:
| Stakeholder | Channel | Frequency |
| Executives | Email reports | Monthly |
| Team | Stand-up meetings | Daily |
| Clients | Video conferences | Fortnightly |
| Partners | Shared dashboards | As needed |
Collaboration tools and techniques
Project management software
Utilise comprehensive project management solutions:
- Gantt charts for timeline visualisation
- Task assignment and tracking
- Resource allocation tools
- Integrated document management.
Team collaboration platforms
Implement platforms that facilitate seamless teamwork:
- Real-time messaging systems
- Virtual whiteboards for brainstorming
- Shared document editing
- Video conferencing capabilities.
By developing robust communication plans and leveraging modern collaboration tools, project managers can enhance team efficiency and stakeholder engagement, ultimately contributing to project success.
Value delivery and continuous improvement
Focus on stakeholder value
Prioritising value-driven tasks
Identify and prioritise tasks that deliver maximum stakeholder value. Conduct regular stakeholder interviews, use value stream mapping. And implement Agile methodologies for rapid value delivery.
Aligning deliverables with stakeholder expectations
Ensure project outputs meet stakeholder needs, It is important to develop clear acceptance criteria, conduct frequent stakeholder reviews and adapt project scope based on feedback.
Lessons learned and project evaluation
Post-project review process
Conduct thorough project retrospectives this includes analysing successes and challenges. Gather feedback from team members and stakeholders. And document key insights and recommendations.
Implementing improvements in future projects
Apply lessons learned to enhance future project performance. Create a knowledge repository, update project management processes and integrate insights into training programmes.
By focusing on value delivery and continuous improvement, project managers can enhance stakeholder satisfaction and organisational performance over time.
Conclusion
Project management principles form the foundation of successful project execution. Key principles include establishing a solid project foundation and defining clear roles and responsibilities. Managing scope and changes effectively. Implementing robust risk management strategies. Monitoring progress through KPIs and baselines. Fostering effective communication and collaboration. And focusing on value delivery and continuous improvement.
Consistent application of these principles is crucial for project success. As the field of project management evolves, practitioners must commit to ongoing learning and adaptation. By embracing these principles and continuously refining their skills, project managers can navigate complex challenges and deliver exceptional results in an ever-changing business landscape.
FAQs
What are the most important project management principles?
Key principles include clear goal setting, effective communication, risk management, and stakeholder engagement.
How can I improve communication in my project team?
Implement a structured communication plan, use collaboration tools, and foster an open feedback culture.
What’s the difference between Agile and traditional project management?
Agile is iterative and flexible, while traditional methods follow a linear, planned approach.
How do I handle scope creep in my projects?
Define clear project boundaries, implement change control processes, and maintain stakeholder alignment.
What are some common project management challenges and how can I overcome them?
Challenges include resource constraints, unclear objectives, and poor communication. Overcome these through careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and continuous improvement.
Infographic