Introduction
Project management is essential for turning ideas into reality. It provides a structured approach to planning, executing and delivering successful outcomes. By following well-defined project management phases, organisations can streamline processes and achieve their goals efficiently.
The importance of project management lies in its ability to optimise resource allocation, minimise risks and uncertainties, improve communication among stakeholders and ensure timely delivery of project objectives.Project management is essential for turning ideas into reality. It provides a structured approach to planning, executing and delivering successful outcomes. By following well-defined project management
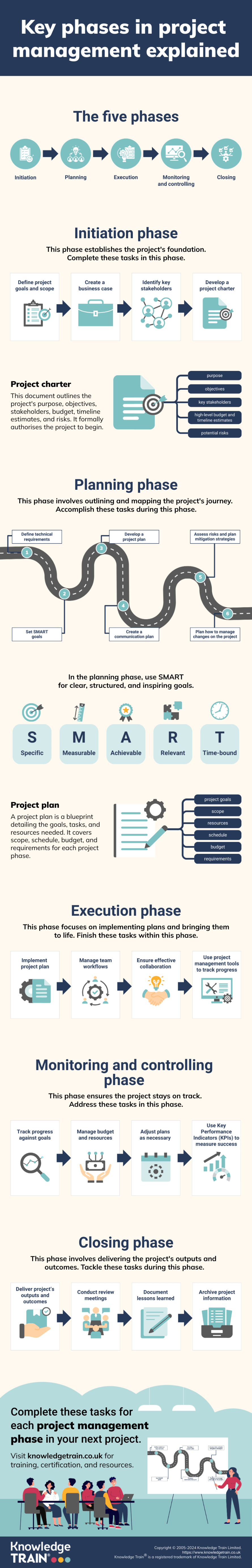
At the core of effective project management are five distinct phases:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Monitoring and controlling
- Closing
Each phase plays a crucial role in guiding a project from conception to completion. Understanding these phases helps project managers navigate challenges and lead their teams to success. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore each phase in detail, providing insights and best practices for effective project management.
The five phases of project management
Understanding the project lifecycle is crucial for effective project management. The five phases provide a structured approach to guide projects from inception to completion.
Brief overview of each phase
- Initiation: Define project goals, scope, and feasibility. Create a project charter and identify key stakeholders.
- Planning: Develop detailed project plans, including timelines, budgets, and resource allocation. Establish communication strategies and risk management protocols.
- Execution: Implement the project plan, manage team workflows, and ensure effective collaboration among stakeholders.
- Monitoring and controlling: Track progress, measure performance against established metrics, and make necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
- Closing: Deliver final outcomes, conduct project reviews, document lessons learned, and archive project information.
Importance of understanding the project lifecycle
Grasping the project lifecycle enables project managers to:
- Anticipate challenges and plan proactively
- Allocate resources efficiently throughout the project
- Maintain clear communication with stakeholders
- Adapt to changes whilst maintaining project integrity
- Ensure consistent quality across all project phases.
By becoming proficient in these phases, project managers can navigate complexities with confidence and deliver successful outcomes.
Project initiation
The project initiation phase sets the foundation for project success. It transforms abstract ideas into actionable goals and establishes the project’s purpose.
Developing a business case
A robust business case justifies the project’s existence and outlines its potential benefits. To create an effective business case:
- Identify the problem or opportunity the project addresses
- Analyse potential solutions and their feasibility
- Estimate costs, benefits, and return on investment
- Present risks and mitigation strategies.
Defining project goals and scope
Clear project goals and a well-defined scope are essential for project success. When defining these elements:
- Ensure goals are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound)
- Outline deliverables and project boundaries
- Identify potential constraints and assumptions.
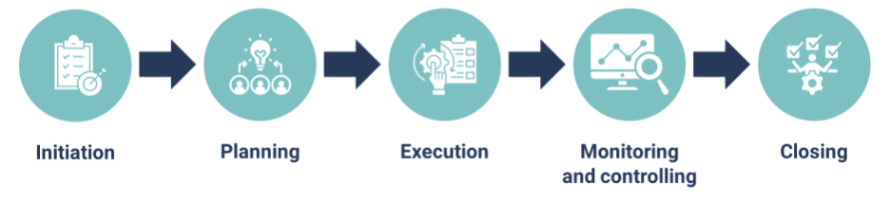
Creating a project charter
The project charter serves as the project’s formal authorisation document. It should include:
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Project purpose | Clear statement of the project’s objectives |
| Scope | High-level description of what’s included and excluded |
| Timelines | Estimated start and end dates |
| Budget | Initial cost estimates |
| Key stakeholders | List of individuals or groups with vested interest |
Identifying key stakeholders
Stakeholder identification is crucial for project success. To effectively manage stakeholders, begin by creating a stakeholder register listing all involved parties then analyse their interests, influence, and potential impact on the project. And develop a communication strategy tailored to each stakeholder group
By thoroughly addressing these elements in the initiation phase, project managers establish a solid foundation for the subsequent phases of the project lifecycle.
Project planning
The planning phase is crucial for project success. It involves creating a comprehensive project plan that guides the project from start to finish.
The project plan builds upon the foundations laid out in the project charter, and covers the technical requirements, the work to be done (in the form of a work breakdown structure), resource planning, and creating a schedule for the work and the major milestones.
Defining technical requirements
Technical requirements outline the specific functionalities and features of the project deliverables. To define these effectively:
- Collaborate with stakeholders to gather requirements
- Prioritise requirements based on importance and feasibility
- Document requirements clearly, avoiding ambiguity
- Validate requirements with relevant experts and end-users.
Developing a detailed project schedule
A well-structured project schedule is essential for timely completion. When creating the schedule:
- Use a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to divide the project into manageable tasks
- Estimate the duration of each task realistically
- Identify dependencies between tasks
- Allocate resources efficiently
- Set milestones to mark significant project progress points.
Creating a communication plan
Effective communication is vital for project success. A comprehensive plan should:
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Stakeholders | Identify all parties involved in communication |
| Frequency | Determine how often updates will be shared |
| Channels | Specify methods of communication (e.g., emails, meetings) |
| Content | Outline what information will be shared |
| Responsibilities | Assign roles for creating and disseminating information |
Setting SMART and CLEAR goals
Combine SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) and CLEAR (Collaborative, Limited, Emotional, Appreciable, Refinable) goal-setting methods for comprehensive project objectives.

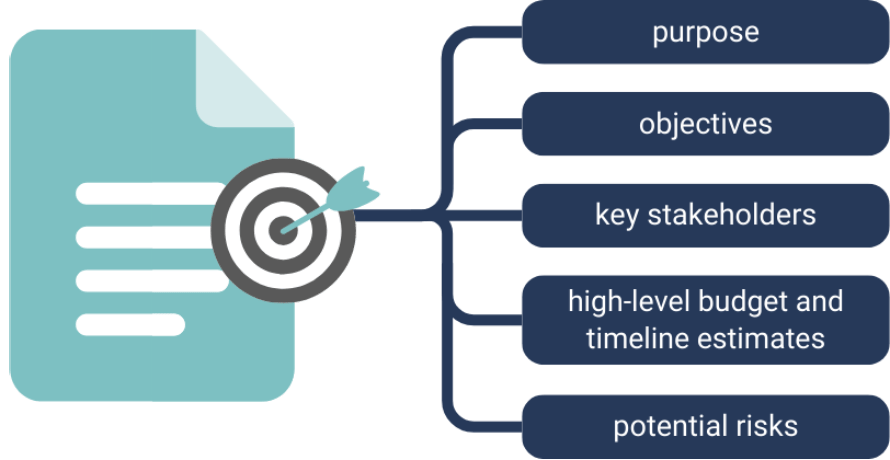
Project plan
In this phase a project plan captures the project goals, scope, resources, schedule, budget, and main requirements for the project. The initial version of the project plan needs to be approved by the project sponsor before proceeding to the next phase and will be updated regularly as the project proceeds.
Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
Effective risk management involves:
- Identifying potential risks
- Assessing their likelihood and potential impact
- Developing mitigation strategies for high-priority risks
- Continuously monitoring and updating risk assessments throughout the project.
Change management planning
Change management is crucial for adapting to evolving project needs. A robust plan should establish a clear process for proposing and approving changes, define roles and responsibilities in the change management process, set criteria for evaluating the impact of proposed changes and create a system for documenting and communicating approved changes.
By thoroughly addressing these elements in the planning phase, project managers lay a solid foundation for successful project execution and delivery.
Project execution
The execution phase is where plans transform into action. This stage requires diligent oversight and effective management to ensure project success.
Implementing the project plan
Executing the project plan involves:
- Assigning tasks to team members based on their skills and availability
- Providing necessary resources and support for task completion
- Monitoring progress against the established timeline
- Addressing issues promptly as they arise.
Managing team workflows
Efficient workflow management is crucial for maintaining productivity. Consider the following strategies:
- Establish clear processes for task handoffs between team members
- Implement Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban for flexible project management
- Conduct regular stand-up meetings to review progress and obstacles
- Encourage open communication to identify and resolve bottlenecks quickly.
Ensuring effective collaboration
Collaboration is key to project success. To foster a collaborative environment:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear roles | Define responsibilities for each team member |
| Open communication | Encourage sharing of ideas and concerns |
| Shared goals | Align team efforts towards common objectives |
| Conflict resolution | Address disagreements promptly and constructively |
Utilising project management tools
Project management tools can significantly enhance execution efficiency. Consider using task management software for tracking progress and deadlines. Collaboration platforms for centralised communication and file sharing. Time-tracking tools to monitor resource allocation and productivity. Reporting dashboards for real-time project status updates
By effectively implementing these strategies during the execution phase, project managers can ensure smooth project progression and maintain team momentum towards achieving project goals.
Project monitoring and controlling
The monitoring and controlling phase ensures that project execution aligns with the established plan. It involves continuous assessment and adjustment to maintain project integrity.
Tracking progress against goals
Effective progress tracking involves:
- Regularly comparing actual performance to planned objectives
- Identifying variances and their root causes
- Implementing corrective actions to address deviations
- Updating stakeholders on project status and any significant changes.
Establishing Critical Success Factors (CSF) and Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
CSFs and KPIs are essential for measuring project success:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| CSFs | High-level goals that must be achieved for project success |
| KPIs | Quantifiable measurements that indicate progress towards CSFs |
To implement these effectively you have to identify CSFs that align with project objectives. Develop KPIs that accurately measure progress towards each CSF and regularly review and update these metrics as the project evolves.
Managing budget and resources
Efficient resource management is crucial for project success, to achieve this, it is essential to monitor expenditure against the allocated budget, track resource utilisation to ensure optimal allocation, identify potential resource constraints or shortages early and implement cost-control measures when necessary.
Adjusting plans as necessary
Plan adjustment is often required to address unexpected challenges, to manage this effectively, conduct regular project reviews to identify areas requiring modification, assess the impact of proposed changes on project scope, timeline and budget, communicate adjustments to all relevant stakeholders and update project documentation to reflect approved changes.
By diligently monitoring and controlling these aspects, project managers can ensure their projects remain on track and adapt effectively to changing circumstances.
Project closing
The closing phase marks the formal conclusion of a project. It involves finalising deliverables, evaluating performance, and documenting insights for future projects.
Delivering final project outcomes
Final delivery entails:
- Ensuring all project deliverables meet agreed-upon specifications
- Obtaining formal acceptance from stakeholders
- Transferring project outputs to the appropriate teams or clients
- Closing any outstanding contracts or agreements.
Conducting project review meetings
Review meetings are crucial for assessing project performance:
- Gather all key stakeholders to evaluate project outcomes
- Evaluate the project’s success against initial objectives
- Identify areas of excellence and opportunities for improvement
• Collect feedback from team members and stakeholders.
Documenting lessons learnt
Capturing lessons learnt is vital for organisational growth:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Successes | Document effective strategies and practices |
| Challenges | Note obstacles encountered and how they were overcome |
| Improvements | Identify areas for enhancement in future projects |
Archiving project information
Proper project archiving ensures valuable information is preserved. To accomplish this, organise all project documentation in a centralised repository, ensure easy accessibility for future reference, include key documents such as project plans, reports, and communications and comply with organisational data retention policies.
By thoroughly addressing these closing activities, project managers can ensure a smooth project conclusion and contribute to ongoing organisational learning and improvement.
Best practices for effective project management
Implementing best practices in project management can significantly enhance project outcomes. These strategies help teams navigate challenges and deliver successful results consistently.
Embracing Agile methodologies
Agile approaches offer flexibility and adaptability in project management:
- Implement iterative development cycles for continuous improvement
- Encourage frequent stakeholder feedback to ensure alignment with goals
- Prioritise tasks based on value and adjust plans as needed
- Foster a culture of collaboration and self-organisation within teams.
Utilising project management software
Project management tools streamline processes and enhance efficiency:
| Tool Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Task management | Organise and track project tasks effectively |
| Collaboration platforms | Facilitate communication and file sharing |
| Resource allocation | Optimise team member workloads |
| Reporting dashboards | Provide real-time project status updates |
Fostering clear communication
Effective communication is crucial for project success:
- Establish clear channels for team and stakeholder communication
- Conduct regular status meetings to keep everyone informed
- Encourage open dialogue to address concerns promptly
- Tailor communication styles to different stakeholders’ needs.
Continuous learning and improvement
Ongoing development enhances project management capabilities:
- Regularly review and analyse project outcomes
- Encourage team members to share insights and lessons learnt
- Stay updated on industry trends and best practices
- Invest in training and professional development opportunities.
By incorporating these best practices, project managers can create a robust framework for successful project delivery. These strategies promote adaptability, efficiency, and continuous improvement throughout the project lifecycle.
Conclusion
Effective project management is essential for achieving organisational goals and delivering successful outcomes. By following the five key phases—initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closing—project managers can ensure a structured approach to project delivery.
Implementing best practices such as embracing Agile methodologies, utilising project management software, fostering clear communication and pursuing continuous learning.
These strategies enhance project success rates and team efficiency. Adhering to these project management phases provides a framework for navigating challenges, optimising resources, and meeting stakeholder expectations. By consistently applying these principles, organisations can improve their project delivery capabilities and achieve better results across all initiatives.
FAQs
What is the most crucial phase of project management?
The planning phase is often considered the most critical. It sets the foundation for project success by defining goals, resources, and timelines.
How can I prevent scope creep in my projects?
To prevent scope creep, clearly define project boundaries, implement a change control process, and regularly review project scope with stakeholders.
What’s the difference between traditional and Agile project management?
Traditional project management follows a linear, sequential approach. Agile methodologies emphasise flexibility, iterative development, and continuous stakeholder feedback.
How often should I conduct project status meetings?
The frequency depends on project complexity and duration. Weekly meetings are common but adjust as needed to balance communication and productivity.
What are some common project management pitfalls to avoid?
Common pitfalls include inadequate stakeholder communication, poor risk management, unrealistic timelines or budgets, lack of clear objectives and insufficient resource allocation.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires careful planning, regular monitoring, and proactive problem-solving throughout the project lifecycle.
Infographic