Introduction
Key Performance Indicators, often referred to as KPIs, are a project management metric set that can help project teams to measure the success of their projects. KPIs are quantitative metrics that can provide project managers with essential insights into the health and progress of a project. Project managers who set and implement effective KPIs can keep track of project performance in an objective way, pinpoint problem areas, take timely corrective action, make well-informed decisions, and also report on their progress to stakeholders.
In this article, we are going to discuss the importance of KPIs for project management. We will also show you how to select the right KPIs for your project, how to successfully implement them in your work processes, and how to use them effectively. We will also take a closer look at the types of KPIs you can use in project management, KPI characteristics, and other tips and best practices.
If you are a project manager or a professional in the field of project management, then KPIs are something you should familiarise yourself with in order to successfully complete projects.
Understanding project management KPIs
Before we discuss the different types of project management KPIs in more detail, it’s important to define the term KPI in the context of project management. We will also look at the key differences between metrics and KPIs.
Definition of KPIs
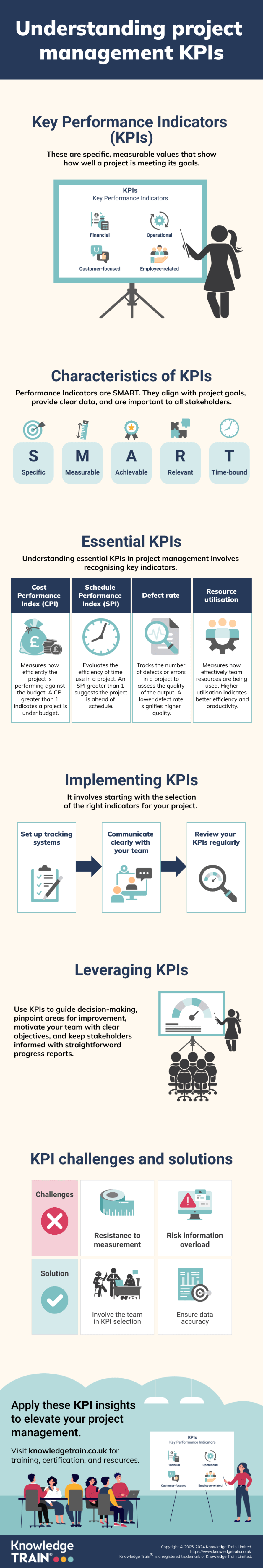
Key performance indicators, often referred to as KPIs, are specific, measurable values that show how effectively a project or initiative is achieving its key objectives. KPIs are used as a guide to keep a project team on track and moving towards its goals.
Difference between metrics and KPIs
All KPIs are metrics, but not all metrics are KPIs. Metrics are a broad set of measurements that projects and organisations can use to measure their performance. KPIs are a subset of metrics and are critical performance indicators directly linked to a project’s success.
Types of KPIs in project management
- Financial KPIs: Monetarily oriented, this set of key performance indicators (KPIs) track financial elements of a project. These include Cost Performance Index (CPI), ROI (Return on investment), and Budget Variance.
- Operational KPIs: Operationally oriented, this set of KPIs monitor the daily project performance. Schedule Performance Index (SPI), Resource Utilisation Rate, Defect Rate are examples.
- Customer-focused KPIs: These indicators are oriented to client satisfaction and value delivery in a project. Customer Satisfaction Score, Net Promoter Score (NPS), On-time Delivery Rate are examples.
- Employee KPIs: Employee-focused KPIs measure the performance and well-being of the project team. Examples include Team Productivity, Employee Satisfaction Index, and Training Effectiveness.
Characteristics of effective project management KPIs
KPIs have specific characteristics which make them better suited to project management. Here is a quick run down on some of the features that you want to see in your performance indicators.
SMART criteria for KPI development
SMART is an acronym commonly used when referring to best practice in developing KPIs. This means that each performance indicator should be: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-based. To develop the best KPIs, you should focus on these five characteristics.
Alignment with project objectives
The first characteristic is that good KPIs are focused on the central goals of the project. In other words, if your project has specific primary objectives that you are trying to reach, your KPIs should measure how close you are to reaching these. This way, you know that when you reach your KPIs, you are making progress on your projects overall.
Measurability and quantifiability
Performance indicators that are quantitative have a major advantage over those that are qualitative. This is because numbers and figures are simple to collect, track, and share.
Most quantitative measures are also easy to compare. This is because numbers have a simple natural order from largest to smallest, allowing you to easily see progress or regress in each of your indicators.
Relevance to stakeholders
The value of a performance indicator is mostly related to how informative it is to those managing a project. In other words, if a KPI does not tell project managers anything they need to know, it is not very useful.
For that reason, the best KPIs are typically both meaningful and informative to all those who have a vested interest in a project.
Time-bound nature
A KPI should also have a set time for which it will be measured and by which it will be achieved. The time factor gives room to track progress and make necessary adjustments to the project.
Addition of the above characteristics will help project managers create KPIs that will give you the most realistic and actionable insight. Meaningful indicators of this kind are a strong weapon to lead your project to success.
Essential project management KPIs
Key performance indicators are vital to project management. They allow managers to get an overall view of how certain aspects of a project are performing. Here is a non-exhaustive list of KPIs essential to project management.
Budget-related KPIs
- Cost performance index (CPI): The CPI is an indicator of how much you are under or over budget in a project. It is measured by dividing the planned cost of work performed by the actual cost. If it is more than one, the project is under budget, and if it is lower than one, it is over budget.
- Budget variance: This KPI calculates the difference between the actual spend and the planned spend. It allows you to detect quickly if you are under or over the budget and when to make financial changes.
Schedule-related KPIs
- Schedule performance index (SPI): The SPI is a measure of how on track you are for meeting the timeline set for the project. The SPI value of 1 indicates that the actual work progress meets the work planned. The SPI is a value greater or less than 1 if the project is ahead or behind the project schedule, respectively.
- On-time completion rate: The on-time completion rate KPI helps you monitor the rate at which tasks or milestones are completed by the due date. This gives you the overview of the project’s timeline adherence and helps you to catch potential delays.
Quality-related KPIs
- Defect rate: The defect rate is the KPI that measures the number of mistakes, errors, and problems in your project output. This KPI, combined with others, helps to measure the quality of the output and indicate if you need to change your process or not.
- Customer satisfaction score: This score is used to measure the clients’ happiness with the result of your work. High customer satisfaction shows successful project delivery and customer expectation management.
Resource-related KPIs
- Resource utilisation rate: The resource utilisation rate measures how much time you spend on your team’s skills. This KPI shows you if there are any bottlenecks or underutilised resources and ways to make it more efficient.
- Team productivity: This KPI measures the efficiency of the team, showing their output for a unit of time or effort. This rate indicates the general productivity and areas that can be improved to raise efficiency.
Monitoring these essential KPIs in projects provides a broad view of how well your project is working. This will help you to take data-driven and timely decisions and manage it proactively for its success.
Implementing KPIs in project management
Applying KPIs is another important stage to fully leverage them in project management. It requires selecting KPIs, tracking them in a structured manner, communicating, and refining them.
Selecting appropriate KPIs for your project
Choose KPIs that align with your project’s specific objectives and constraints. Consider the project’s scope, industry, and stakeholder expectations. Limit your selection to a manageable number of key indicators to maintain focus and prevent data overload.
Setting up KPI tracking systems
Implement systems to consistently collect and track data for each KPI. Utilise project management software or tools that allow you to monitor KPIs in real-time. Ensure data accuracy by establishing clear guidelines for data collection and reporting. Regularly review and update your KPI tracking processes to adapt to project changes.
Communicating KPIs to team members and stakeholders
Share the selected KPIs with your team members and stakeholders. Clearly communicate the purpose, expected outcomes, and target values for each KPI. Use visual representations, such as dashboards or charts, to make KPIs easily understandable. Regularly update stakeholders on KPI performance to maintain transparency and foster engagement.
Regular review and adjustment of KPIs
Continuously monitor the progress of your KPIs throughout the project. Track data on a regular basis and compare it against the set targets. Analyse trends, identify deviations, and take corrective actions when necessary. Be open to adjusting KPIs if they no longer align with the project’s direction or if new priorities emerge.
Leveraging KPIs for project success
With the help of KPIs, your team can influence and drive success on projects more often. Use them in the areas below to make them work harder for your projects’ success.
Using KPIs for decision-making
Project KPIs should be reviewed when faced with a critical decision that can significantly impact the project. Reference relevant KPIs and use the objective data to inform your decision-making process. This approach will help to reduce subjective bias and increase the quality of the decision.
Identifying areas for improvement
Review KPIs regularly to identify gaps in performance and areas where improvement can be made. Conduct a trend analysis on project KPIs to identify any patterns, including recurring issues or bottlenecks, and make adjustments to processes where needed.
Motivating team members through KPI-based goals
Align individual and team goals with project KPIs, and set challenging but achievable KPI-based targets to motivate performance. Recognise and reward team members for meeting and exceeding these targets to foster a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
Reporting project progress to stakeholders
Use KPIs to generate progress reports for stakeholders in a clear, concise format. Visualise KPI data to effectively communicate project status and trends. Regular updates based on KPIs can build trust and keep stakeholders engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
In summary, by using KPIs as described in this article, project managers can make more informed decisions, drive improvements, motivate team members and maintain strong relationships with stakeholders, which significantly improves the chance of success of a project.
Common challenges and solutions in KPI implementation
While KPIs are powerful, their implementation can encounter challenges. Here’s how to navigate common obstacles.
Overcoming resistance to measurement
Team members may feel anxious about being measured. Address these concerns by emphasising KPIs as tools for improvement, not punishment. Involve team members in the selection of KPIs to increase buy-in and understanding.
Avoiding information overload
Presenting too many KPIs can overwhelm and confuse. Focus on a limited set of critical KPIs directly tied to project objectives. Use dashboards to display data clearly and concisely, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
Ensuring data accuracy and reliability
KPIs are only as good as the data behind them. Establish rigorous data collection and validation processes to ensure accuracy. Regularly audit your KPI data sources and calculation methods for consistency and correctness. Invest in reliable project management software that automates data gathering, reducing the potential for human error.
By proactively addressing these challenges, project managers can ensure KPIs are implemented and used effectively.
Conclusion
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are critical tools for the project manager. By providing an objective measure of a project’s health and progress, KPIs allow for data-driven decision-making and proactive project management.
To use KPIs effectively, it is important to select the right indicators, track them consistently, and review them regularly. When done well, KPIs can significantly improve project outcomes and align with the expectations of stakeholders.
We encourage you to implement KPIs into your project management practices. Begin by identifying the most relevant indicators for your projects and establishing systems for measuring and analysing them. Remember that the goal is continuous improvement, not perfection. With careful and diligent application of KPI practices, you can guide your projects towards greater success and efficiency.
FAQs
What is the difference between a KPI and a metric in project management?
KPIs are metrics that are directly linked to key project goals, while metrics are measurements used more generally.
How many KPIs should I use for my project?
Generally, 5-7 key KPIs are enough. It is more important to choose the right KPIs than to have a large number of KPIs which may just add to information overload.
How often should I review and update my project KPIs?
Review and update your project KPIs on a monthly or quarterly basis, or as the needs of the project change.
Can KPIs be used in Agile project management?
Yes, KPIs are a useful tool for Agile project management, particularly for measuring sprint and release performance.
How do I align my project KPIs with overall business objectives?
Talk to key stakeholders and refer to your organisation’s strategy when deciding on project KPIs, in order to ensure they are aligned with overall business objectives.
Infographic