Introduction
A Project Management Office (PMO) is a centralised department that standardises project-related governance processes and facilitates resource sharing, methodologies, tools, and techniques. PMOs are essential for ensuring strategic alignment of projects, optimising resource utilisation, and enhancing project success rates.
This article examines the various PMO roles, their responsibilities, and their contributions to organisational success. We’ll explore different PMO types, compare PMO functions to those of project managers, and consider emerging trends. Understanding these aspects can help organisations effectively use PMOs to improve efficiency and achieve strategic objectives.
Types of PMO
PMOs can be categorised based on their scope and function within an organisation. Understanding these types helps in implementing the most suitable PMO structure.
- Project Management Office: Focuses on supporting individual projects, providing guidance and best practices to project managers.
- Programme Management Office: Oversees related projects aligned with a specific programme or objective, managing interdependencies and conflicts.
- Portfolio Management Office: Manages the entire portfolio of projects and programmes, allocating resources and prioritising initiatives based on strategic objectives.
- Enterprise-level PMO: Aligns all project management tasks with the organisation’s overall strategy and goals across all departments.
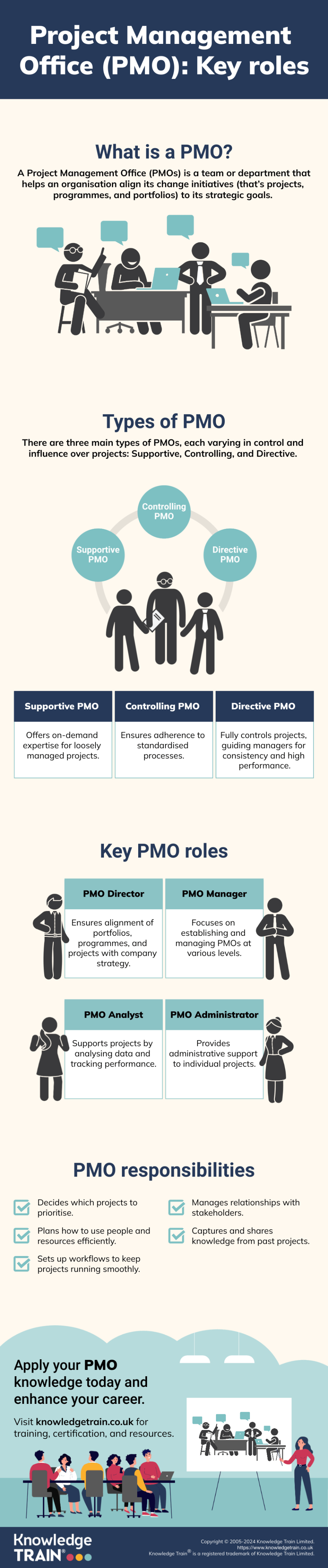
- Supportive PMO: Acts as a consultative entity, providing guidance and support to project managers as needed.
- Controlling PMO: Enforces project management processes and standards, reviewing and approving project plans.
- Directive PMO: Assumes a decision-making role with a high degree of control over projects, including resource allocation and budget management.
Each PMO type serves different organisational needs and structures. The choice depends on factors such as company size, industry, and strategic objectives.
Key PMO roles and responsibilities
A well-structured PMO comprises several key roles, each contributing to the overall effectiveness of project management within an organisation. Let’s examine these roles and their primary responsibilities:
PMO director
The PMO director is a senior-level executive responsible for:
- Strategic alignment: Ensuring that all projects align with the organisation’s strategic goals and objectives. This involves collaborating with senior management to understand business priorities, evaluating project portfolios for strategic fit, and recommending adjustments to project portfolios as needed.
- Oversight of PMO function: Managing the overall performance and direction of the PMO. This includes setting PMO policies and standards, monitoring PMO effectiveness, and reporting on PMO performance to senior management.
PMO manager
The PMO manager focuses on:
- Day-to-day management: Overseeing the PMO’s daily operations and ensuring smooth functioning. This involves coordinating PMO activities, managing PMO staff, and addressing operational issues as they arise.
- Process implementation: Establishing and maintaining project management processes and methodologies. This includes developing and updating project management templates and tools, ensuring compliance with established processes, and identifying areas for process improvement.
PMO analyst
The PMO analyst is responsible for:
- Data analysis: Collecting and analysing project data to provide insights. This involves gathering data from various project sources, conducting trend analysis and identifying patterns, and preparing analytical reports for decision-making.
- Performance metrics: Developing and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) for projects and the PMO. This includes establishing relevant KPIs, monitoring project and portfolio performance against KPIs, and recommending corrective actions based on performance data.
PMO consultant
The PMO consultant provides:
- Strategic advice: Offering expert guidance on project management best practices and methodologies. This involves assessing current project management practices, recommending improvements and optimisations, and providing guidance on complex project issues.
- Best practices implementation: Assisting in the adoption of industry-standard project management approaches. This includes identifying relevant best practices, developing implementation plans, and training project teams on new methodologies.
PMO administrator
The PMO administrator is responsible for:
- Administrative support: Providing operational assistance to the PMO and project teams. This involves scheduling meetings and managing calendars, assisting with resource allocation, and maintaining PMO records and files.
- Documentation management: Ensuring proper documentation of project-related information. This includes creating and updating project documentation, managing document version control, and maintaining the project management information system.
Core PMO responsibilities
The PMO plays a crucial role in ensuring project success and organisational efficiency. Here are the core responsibilities that define the PMO’s function:
Project prioritisation and governance
The PMO is responsible for developing project selection criteria aligned with organisational goals, evaluating and ranking projects based on strategic importance and resource availability, implementing a governance framework to guide project execution and monitoring, and establishing risk management protocols and quality assurance processes.
Resource planning and scheduling
Effective resource management is a key PMO function, involving forecasting resource demand for upcoming projects, assessing available resources and their skill sets, identifying resource gaps and developing comprehensive resource plans, and creating and maintaining project schedules to optimise resource allocation.
Resource optimisation
The PMO ensures efficient utilisation of resources by tracking resource usage across projects and identifying instances of over or underutilisation, implementing strategies to balance workloads and prevent burnout, recommending skill development initiatives to enhance resource capabilities, and facilitating resource sharing across projects and departments.
Workflow management
PMOs streamline project execution through establishing standardised workflows for various project processes, implementing project management tools and technologies, continuously evaluating and improving operational efficiency, and ensuring seamless communication and collaboration among project teams.
Stakeholder management
The PMO facilitates effective stakeholder engagement by identifying key stakeholders and their interests, developing communication strategies tailored to different stakeholder groups, coordinating regular status updates and progress reports, and managing stakeholder expectations and addressing concerns promptly.
Knowledge management
A critical PMO responsibility is capturing and sharing project knowledge:
- Maintaining a centralised repository of project plans, templates, and best practices
- Facilitating lessons learned sessions to capture insights from completed projects
- Developing and delivering training programs to enhance project management skills
- Promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement within the organisation.
By fulfilling these core responsibilities, the PMO contributes significantly to project success, resource efficiency, and overall organisational effectiveness. It serves as a central hub for project-related information and expertise, enabling informed decision-making and consistent project delivery.
PMO vs project manager
While both PMOs and project managers contribute to project success, their roles and responsibilities differ significantly:
Scope of responsibility
- PMO: Establishes and maintains project management standards across the organisation
- Project manager: Manages specific projects within defined constraints.
Governance
- PMO: Provides oversight and support for multiple projects
- Project manager: Manages stakeholders at the project level.
Stakeholder management
- PMO: Creates and maintains organisation-wide knowledge repositories
- Project manager: Documents project-specific lessons and best practices.
Knowledge management
- PMO: Creates and maintains organisation-wide knowledge repositories
- Project manager: Documents project-specific lessons and best practices.
Performance measurement
- PMO: Establishes KPIs and metrics for overall project and portfolio performance
- Project manager: Monitors project performance against predefined objectives.
Understanding these distinctions helps organisations leverage both roles effectively. The PMO focuses on standardisation and strategic alignment, while project managers ensure successful delivery of individual projects. This synergy between PMOs and project managers enhances overall project management effectiveness and organisational success.
Benefits of implementing a PMO
Implementing a PMO offers numerous advantages to organisations. Let’s explore the key benefits:
Real-time visibility across the enterprise
A PMO provides a centralised data collection from various sources, customised dashboards for different stakeholders, and up-to-date insights on project progress and performance.
This visibility enables quick identification of issues and timely decision-making.
Reduced project resourcing costs
PMOs contribute to cost reduction by allocating the right resources to projects at optimal times, minimising last-minute, expensive recruitment, and ensuring timely project completion, improving customer satisfaction.
Optimal resource utilisation
PMOs enhance resource efficiency through tracking future resource demand and forecasting utilisation, proactively mobilising resources from non-billable to billable work, and identifying and addressing instances of over or underutilisation.
This approach maximises productivity and prevents employee burnout.
Improved business decision-making
PMOs facilitate better decisions by tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics, providing data-driven insights for strategic planning, and enabling proactive identification of trends and potential issues.
These capabilities support informed decision-making at all organisational levels.
Future-proofing the workforce against market volatility
PMOs help organisations adapt to market changes by conducting capacity planning to forecast resource needs, creating an optimal mix of permanent and contingent employees, and developing strategies to mitigate risks in changing market conditions.
This forward-thinking approach ensures organisational resilience and adaptability.
By leveraging these benefits, organisations can significantly enhance their project management capabilities, improve operational efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives more effectively.
Establishing a successful PMO
Creating an effective PMO requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to establish a successful PMO:
Assess current project management state
Effectively assessing the current state of project management involves evaluating existing practices and methodologies, identifying strengths and areas for improvement, and gathering feedback from project teams and stakeholders.
Define PMO purpose and objectives
Establishing a strong basis for the PMO involves defining its purpose and objectives by aligning its goals with the organisational strategy, specifying its role in enhancing project management, and setting clear, measurable objectives.
Recruit the right professionals
Building a high-performing team involves recruiting the right professionals by hiring experienced project management experts, ensuring a mix of technical and soft skills, and considering certifications and industry experience.
Create a PMO charter
Develop a comprehensive PMO charter that outlines the PMO’s scope, responsibilities, and authority, defines reporting structures and stakeholder relationships, and documents resource requirements and budget allocations.
Choose appropriate PMO model
Determine the best PMO model for your organisation by selecting one that fits the organisational needs, such as supportive, controlling, or directive, while considering factors like company size, industry, and project complexity, and ensure that the chosen model aligns with the organisational culture.
Develop standardised processes
Establish robust project management practices by creating consistent project management methodologies, implementing tools and templates for project execution, and establishing clear communication channels and reporting mechanisms.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
For reliable measurement of performance, establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) by defining metrics to measure both PMO and project success, aligning KPIs with organisational goals, and implementing systems for tracking and reporting on these indicators.
By following these steps, organisations can create a robust PMO that drives project success and supports strategic objectives.
Future trends in PMO
The PMO landscape is evolving to meet changing business needs. Key trends include:
- Hybrid methodologies: PMOs are blending traditional and agile approaches for greater flexibility and adaptability.
- AI and automation: Advanced technologies are streamlining operations, enhancing forecasting, and optimising resource allocation.
- Innovation focus: PMOs are fostering creativity through innovation labs and cross-functional collaboration platforms.
- Holistic resource management: Emphasis is shifting towards comprehensive resource utilisation across projects and departments.
- Real-time business intelligence: PMOs are leveraging customised data analytics for improved decision-making and performance monitoring.
These trends reflect the PMO’s growing strategic importance. By embracing these advancements, PMOs can enhance their value proposition, driving organisational efficiency and project success. As the business landscape evolves, PMOs must adapt to remain effective and relevant in supporting organisational goals.
Conclusion
The PMO plays a crucial role in modern organisations, offering strategic oversight and operational support. PMOs enhance project success rates, optimise resource utilisation, and align projects with business objectives. As we’ve explored, PMO roles range from directors to analysts, each contributing unique value.
Looking ahead, PMOs will continue to evolve, embracing hybrid methodologies, AI-driven automation, and data-centric approaches. The future PMO will be more agile, innovative, and strategically aligned with organisational goals. By adapting to these trends, PMOs will remain indispensable in driving project success and organisational efficiency in an increasingly complex business landscape.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of a PMO?
To standardise project management processes and ensure strategic alignment of projects with organisational goals.
How does a PMO differ from a project management team?
A PMO oversees multiple projects, while a project management team focuses on specific project execution.
What skills are essential for PMO professionals?
Leadership, analytical thinking, communication, and strategic planning are crucial.
Can small organisations benefit from implementing a PMO?
Yes, PMOs can be scaled to fit organisations of any size, offering benefits in efficiency and project success.
How does a PMO contribute to project success rates?
By providing standardised processes, best practices, and strategic oversight.
What tools do PMOs typically use?
Project management software, data analytics platforms, and collaboration tools.
How can a PMO adapt to Agile methodologies?
By implementing hybrid approaches and fostering a culture of flexibility and continuous improvement.
Infographic