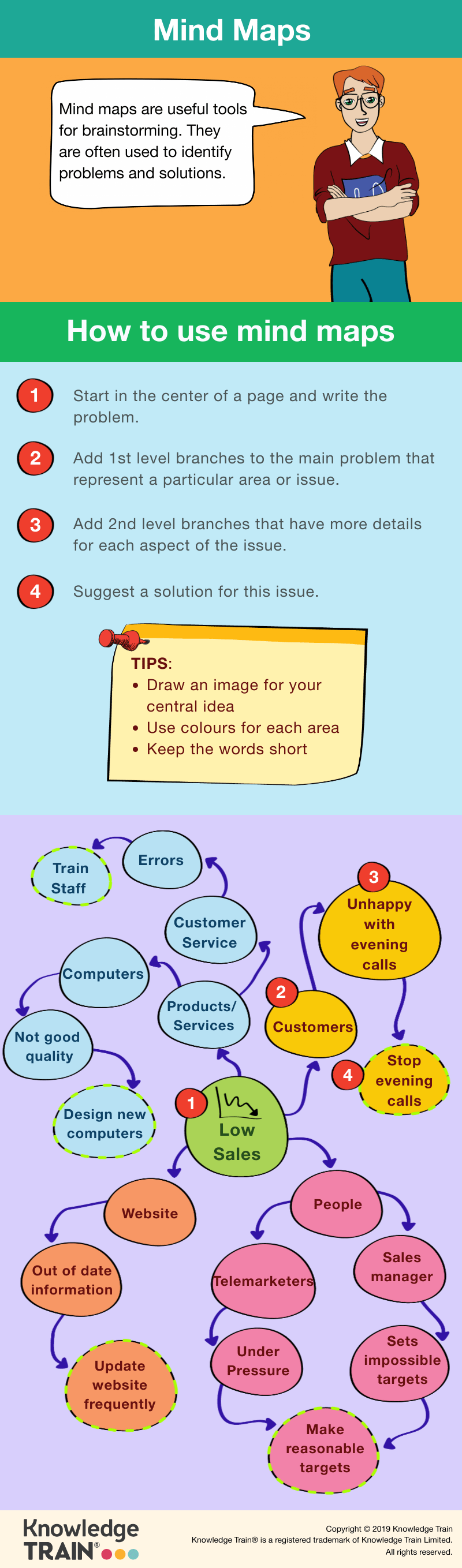
Introduction to mind maps

Definition and purpose of mind maps
A mind map is a visual tool designed to organise and structure information in a non-linear manner. It begins with a central concept, typically represented as a word or phrase, from which related ideas branch out. These branches can contain subtopics and further details, creating a clear and hierarchical representation of information. Mind maps are valuable for visualising complex ideas, fostering creativity and supporting memory retention, though effectiveness varies by individual learning style. They are widely used across various fields, including education, business, and creative writing, to streamline thought processes and improve clarity.
Historical background
While similar visual mapping techniques existed earlier, British author and educational consultant Tony Buzan developed and popularised modern mind mapping in the 1970s, specifically introducing the term ‘mind map’ in 1974. Buzan advocated for mind maps to unlock the potential of the human brain, drawing inspiration from the way the brain naturally processes information. Over time, mind mapping has evolved significantly, integrating technology and digital tools to cater to modern needs. Today, mind maps are a staple in both personal and professional settings, offering a dynamic way to organise thoughts and ideas in a visually engaging format. This evolution underscores their enduring relevance and adaptability in an ever-changing world.
The science behind mind mapping
Cognitive benefits
Mind maps are a powerful tool for enhancing memory retention and cognitive processing. They can support visual learning and association, potentially making it easier to remember and retrieve information for many individuals. By structuring information visually, mind maps help to establish connections between concepts, facilitating a deeper understanding of the material. This process engages multiple cognitive functions, promoting a holistic approach to learning. Some studies suggest that using mind maps may improve recall by enabling individuals to visualise the relationships between ideas. Furthermore, mind maps encourage active engagement with the material, which is crucial for effective learning and comprehension. This visual representation of ideas supports the brain’s ability to synthesise and integrate information, ultimately leading to enhanced cognitive performance.
Psychological impact
The use of mind maps also offers significant psychological benefits. They provide a structured yet flexible framework that can help reduce stress, particularly when dealing with complex or overwhelming information. By breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable parts, mind maps can alleviate feelings of anxiety and enhance focus. This method of organisation fosters a sense of control and clarity, allowing individuals to approach tasks with confidence. Additionally, mind maps stimulate creativity by encouraging the exploration of multiple ideas and perspectives. This creative freedom can lead to innovative solutions and insights, making mind mapping a valuable tool in both personal and professional contexts. By visually organising thoughts and ideas, mind maps not only improve cognitive function but also support psychological well-being, offering a comprehensive approach to managing information and enhancing productivity.
Creating a mind map
Tools and techniques
Creating a mind map begins with choosing the right tools and techniques to suit your needs. Traditional methods involve using pen and paper to draw out your map, which can be highly effective for those who prefer a tactile approach. This method encourages a hands-on interaction with ideas, allowing for spontaneous changes and additions.
For those who prefer digital solutions, several software options are available that offer flexibility and convenience. Digital tools such as MindMeister, XMind, and Miro allow users to create complex maps with ease, offering features like templates, collaboration options, and the ability to integrate multimedia elements.
Regardless of the tool chosen, the fundamental technique remains consistent. Start with a core theme at the centre. This central concept serves as the anchor for your map. From this point, branch out into subtopics that relate directly to the central theme. Each branch can further divide into smaller themes, allowing for a detailed exploration of ideas. The flexibility of this approach means there are no limits to the depth of your mind map.
Step-by-step guide
Creating a mind map follows a straightforward process, which can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Identify the central theme: Begin by determining the primary concept or theme you wish to explore. This could be a project, a topic for an essay, or any idea you want to expand upon.
- Create initial branches: Identify three to five subtopics related to your central theme. These will form the starting branches of your mind map. Each subtopic should represent a significant aspect of the central theme.
- Develop sub-branches: For each initial branch, add further sub-branches to explore related ideas in greater detail. This step allows you to organise information hierarchically, making complex information more manageable.
- Incorporate keywords and visuals: Use concise keywords to label each branch and sub-branch. Where possible, include images, symbols, or colour coding to enhance memory and understanding.
- Review and revise: Once the mind map is complete, review it to ensure all relevant ideas are included and logically arranged. Adjust as necessary to improve clarity and coherence.
By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive and visually engaging mind map that effectively organises and communicates your ideas.
Applications of mind maps
Educational use
Mind maps are a valuable tool in educational settings, where they enhance both learning and note-taking. By visually organising information, students can better understand and remember complex topics. The process of creating hand-drawn mind maps encourages active engagement, allowing students to personalise their learning. This method is particularly effective for brainstorming, revising, and summarising information, making it an essential strategy for effective study habits.
Professional and personal use
In the professional realm, mind maps are instrumental in creative writing and content creation. Writers utilise mind maps to structure their ideas, develop characters, and plot narratives. By visualising thoughts and connections, they can organise content more coherently and creatively. This approach aids in overcoming writer’s block and encourages innovative storytelling.
In project management, mind maps provide a clear overview of tasks and objectives. They allow teams to break down projects into smaller, manageable components, aiding in efficient planning and execution. By mapping out project timelines, resources, and responsibilities, teams can ensure that all aspects of a project are covered, enhancing collaboration and productivity.
For personal organisation, mind maps offer a flexible way to plan goals and manage time. They help individuals organise their daily tasks, set priorities, and track progress. This visual method of organisation can reduce stress by providing a clear structure for managing personal and professional responsibilities. Mind maps can also be used for decision-making, enabling individuals to weigh options and outcomes visually.
Overall, mind maps serve as a versatile tool across various fields, accommodating the diverse needs of individuals and teams. Whether for educational, professional, or personal purposes, mind maps offer a structured yet flexible method to organise thoughts and achieve clarity and efficiency.
Tips for effective mind mapping
Maximising clarity and readability
To enhance the clarity of your mind map, focus on using concise keywords that capture the essence of each idea. This approach makes the map easier to read and understand. Organise your branches logically, ensuring each level of the map builds on the previous one. Colour coding different branches can further aid in distinguishing between various themes and topics, making the overall structure more intuitive. Utilising consistent symbols or images can also enhance visual appeal and support memory retention.
Avoiding common mistakes
One common mistake in mind mapping is overcrowding the map with too much information, which can lead to confusion. To avoid this, maintain a clear hierarchy and limit the number of branches to prevent clutter. Another pitfall is neglecting to review and revise the map. Regularly updating your mind map ensures it remains relevant and useful. Additionally, ensure that all connections between branches are logical and coherent. This practice will help in maintaining the integrity of the map and achieving your intended objectives. By being mindful of these potential issues, you can create effective and meaningful mind maps that serve their intended purpose.
Future of mind mapping
Technological advancements
The future of mind mapping is poised for transformation through technological advancements. With the integration of artificial intelligence, mind mapping tools can offer personalised suggestions, enhancing idea generation and organisation. Virtual reality may also play a role, providing immersive 3D environments for an enriched mapping experience. Cloud-based platforms are likely to improve collaborative capabilities, allowing real-time updates and teamwork across global locations. As these technologies evolve, mind mapping tools will become more intuitive and adaptable, further embedding themselves in educational, professional, and personal contexts. This evolution promises to make mind mapping even more accessible and effective.
FAQs
What is a mind map and how does it work?
A mind map is a visual tool that organises ideas around a central theme. It uses branches to explore related subtopics and concepts.
What are the benefits of using mind maps in education?
Mind maps enhance learning by visually organising information, improving comprehension and memory retention.
How can mind maps improve productivity in the workplace?
They aid in project management by breaking down tasks, clarifying objectives, and fostering collaboration.
What tools are recommended for creating digital mind maps?
Popular tools include MindMeister, XMind, and Miro.
Are there any limitations to using mind maps?
They can become cluttered if not well-organised and may be less effective for linear information.
Infographic